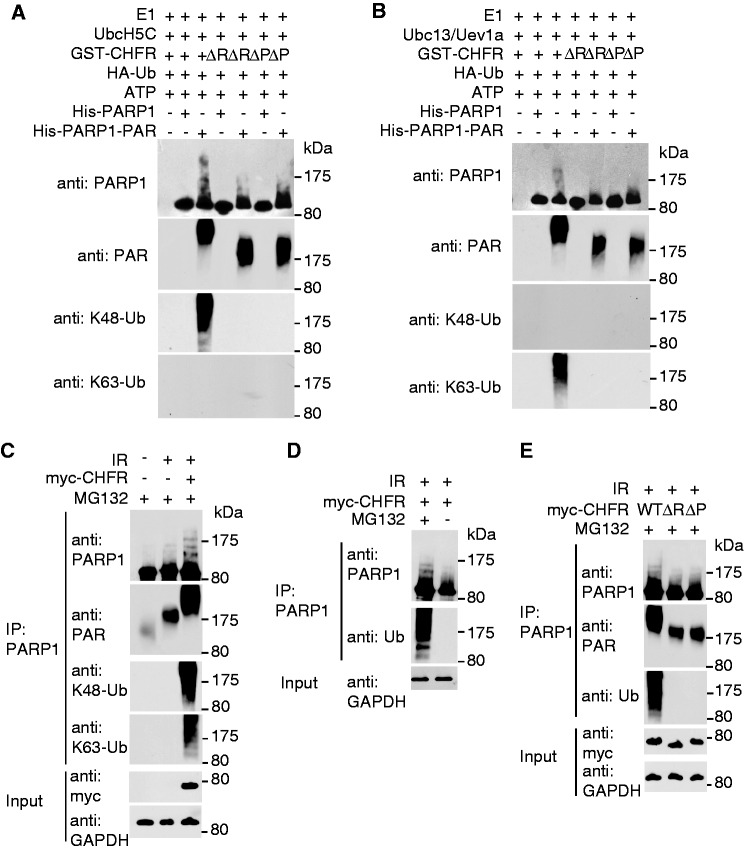
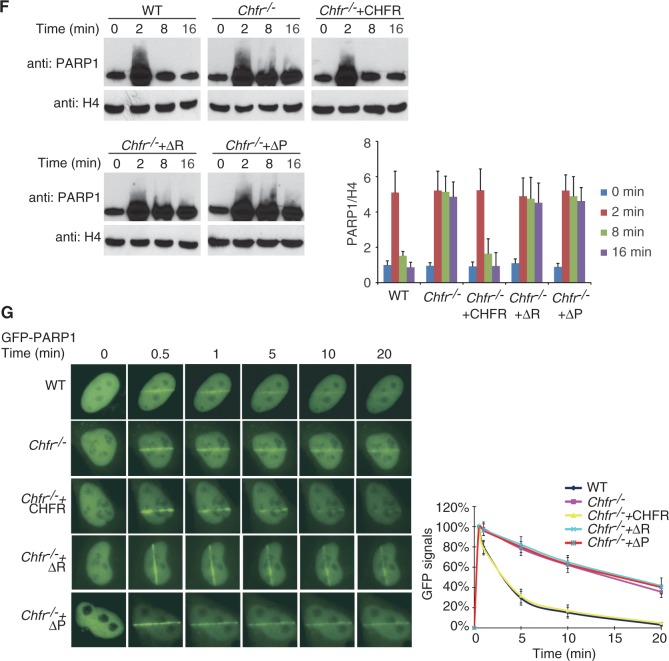
Figure 4.
CHFR ubiquitinates PARylated PARP1 and regulates the chromatin-associated PARP1 following DNA damage. (A and B) CHFR ubiquitinates PARylated PARP1 in vitro. In vitro ubquitination assay was performed using His-PARP1 or PARylated His-PARP1 as the substrates. Ubiquitinated proteins were examined by SDS–PAGE and western blot by using anti-PARP1, anti-PAR, anti-K48 and anti-K63 poly-ubiquitin chain antibodies. (A) UbcH5c was used as E2 conjugase. (B) Ubc13/Uev1a was used as E2 conjugase. (C) CHFR regulates PARP1 ubiquitination in vivo. HCT116 cells expressing myc-CHFR or mock plasmids were treated with 10 Gy of IR in the presence of 10 µM MG132. PARP1 was immunoprecipitated from the cell lysates and subjected to SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-PARP1, anti-PAR, anti-K48 and anti-K63 poly-ubiquitin chain antibodies. (D) HCT116 cells expressing myc-CHFR were treated with 10 Gy of IR in the absence or presence of MG132. PARP1 was immunoprecipitated from the cell lysates and analysed by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-PARP1 and anti-Ub (FK2) antibodies. (E) HCT116 cells expressing myc-tagged wild-type CHFR, the RING domain or PBZ motif deletion mutants were treated with 10 Gy of IR in the presence of MG132. PARP1 status was examined by indicated antibodies. (F) The chromatin retention of PARP1 is regulated by the E3 ligase activity and PAR-binding ability of CHFR. The chromatin-associated PARP1 was examined at the indicated time points following 10 Gy of IR treatments. The displacement of PARP1 from the chromatin was restored in Chfr−/− MEFs reconstituted with wild-type CHFR but not the RING domain or PBZ motif deletion mutants. Histone H4 was blotted as input control for chromatin-associated proteins. The relative amount of PARP1 in the chromatin fraction was quantitatively analysed. The data were obtained from three independent experiments and bar stands for SD. (G) The retention of GFP-PARP1 at DNA damage sites in wild-type (WT), Chfr−/− or Chfr−/− MEF reconstituted with wild-type CHFR, the RING domain deletion mutant or the PBZ motif deletion mutant was examined. The highest GFP intensity was calculated as 100% in each cell, and kinetics of the recruitment were plotted. Data were analysed from 20 cells in each experiment. Data were presented as mean ± SD. ΔR, RING domain deletion mutant of CHFR; ΔP, PBZ motif deletion mutant of CHFR. Bar, 10 µm.