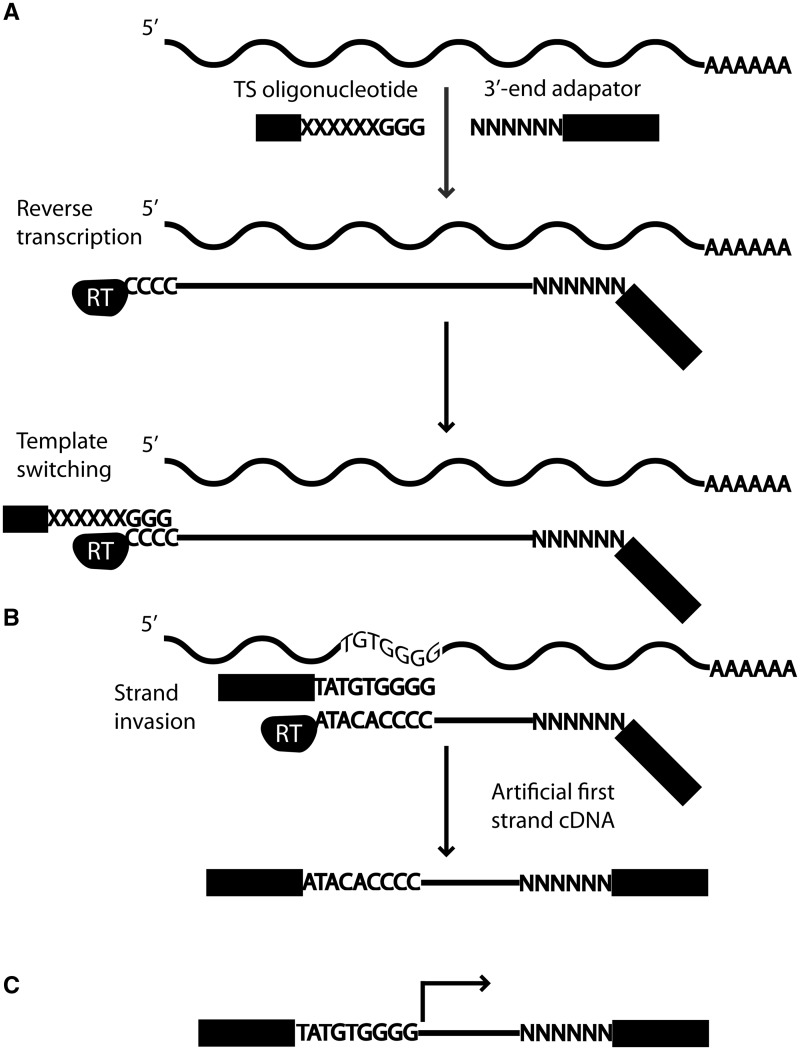
Figure 1.
(A) The TS mechanism is used for first strand cDNA synthesis. First, an oligonucleotide hybridizes to the RNA molecule, and RT starts polymerizing. Once the RT reaches the 5′ end of the RNA, a cytosine overhang is formed. The TS oligonucleotide containing three riboguanosines hybridizes to the cytosine overhang and the RT switches template and polymerizes the TS oligonucleotide. (B) However, during RT synthesis, if the polymerized region has sequence complementary with the 3′ tail of the TS oligonucleotide, it may invade and hybridize with the first strand cDNA. RT then switches template and polymerizes the TS oligonucleotide. However, this strand invasion process has resulted in a cDNA that is shorter than the RNA. (C) With the nanoCAGE protocol, sequencing begins just upstream of the site of TS, which includes the barcode and the riboguanosine linker sequence. The barcode and linker sequences are trimmed off during processing steps, and the final read sequence is indicated by the black arrow.