Figure 4.
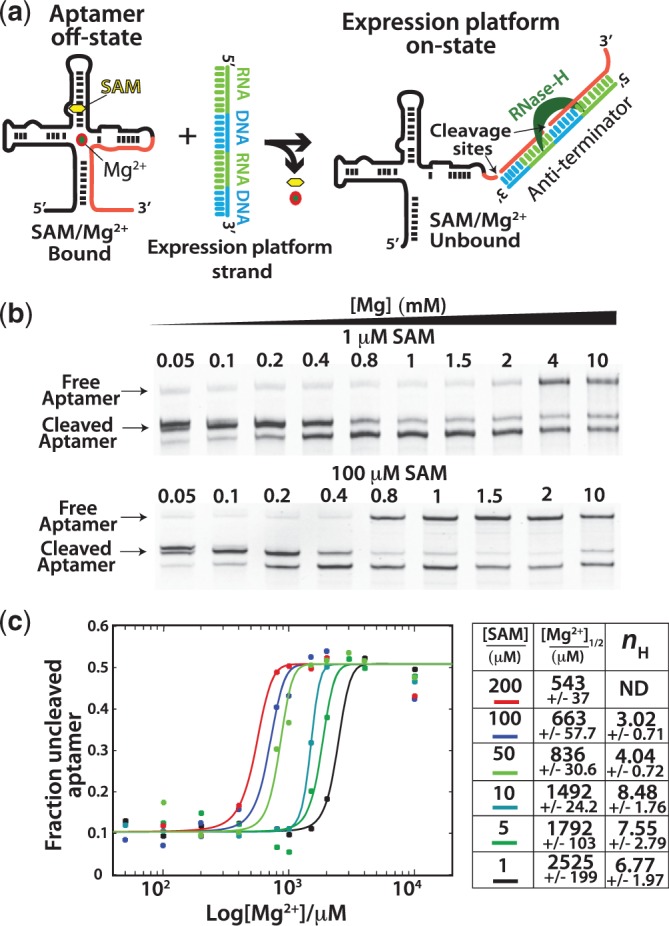
Switching assay results. (a) Aptamer domain RNA is folded and challenged with a chimeric RNA/DNA oligomer based on the native expression platform sequence. Instability in the aptamer domain allows the expression platform sequence to compete for shared sequence in the aptamer domain. Formation of the anti-terminator helix produces a substrate RNA–DNA duplex for RNase H resulting in cleavage of the aptamer domain (right). (b) Example denaturing PAGE gels used to analyse the Mg2+ titrations at various concentrations of SAM. Mg2+ concentrations were chosen for each SAM concentration to best resolve the transition from destabilized (cleaved) to stable (uncleaved) aptamer. (c) After quantification of the bands representing the cleaved (sum of both cleavage products) and uncleaved fractions, the data [(fluorescence uncleaved aptamer)/(fluorescence cleaved + uncleaved aptamer)] were plotted versus [Mg2+] and fit to the Hill equation (methods, equation 2). Fits yielded the [Mg2+]1/2 (the concentration at which the transition was 50% complete) and Hill coefficients (nH) for the transitions at each concentration of SAM. Fits to the Hill model were performed on representative data sets, and errors represent the standard errors for the fitting of that parameter. Hill coefficients were not determined for the experiments with 200 µM SAM. High fit errors were caused by too few data points representing fully cleaved aptamer at low Mg2+ concentrations (standard errors exceeded 100%).
