Fig 5.
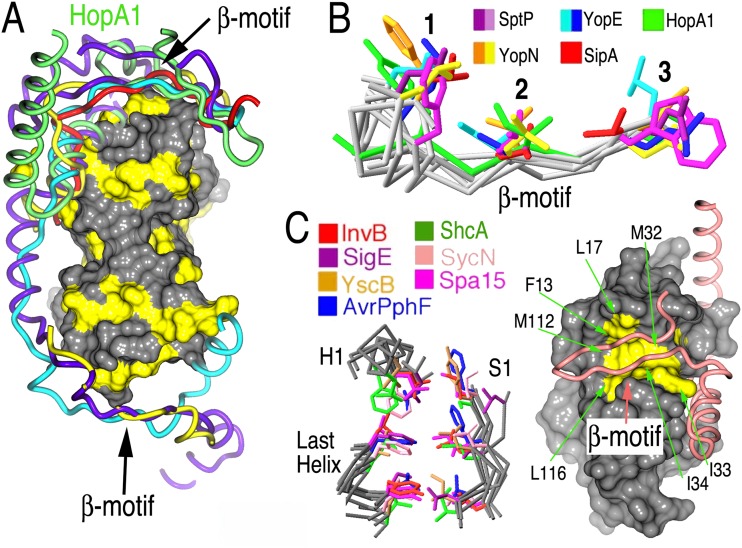
HopA1 possesses a β-motif analogous to virulence factors of animal pathogens. (A) Comparison of T3SS effector nonglobular polypeptides from several complexes with chaperones (alignment was generated by aligning the complexes based on the chaperone-conserved folds). The effector polypeptides include Salmonella SipA (PDB accession number 2FM8) (red) and SptP (PDB accession number 1JYO) (purple), Yersinia YopN (PDB accession number 1XKP) (yellow) and YopE (PDB accession number 1L2W) (cyan), and Pseudomonas syringae HopA1 (green). A surface rendering of ShcA, with the hydrophobic patches shown in yellow, is presented to orient the image. (B) Alignment of several β-motifs from animal and plant effectors. (C) Alignment of β-motif binding pockets in chaperones from animal and plant pathogens. Left, three key elements of the structure in all chaperones characterized to date, consisting of six highly conserved hydrophobic amino acids which closely superimposed and frequently make contacts with β-motif residues. Right, space-filling representation of ShcA, with the six conserved hydrophobic residues of the chaperone pocket shown in yellow and indicated by arrows. The main chain trace of HopA1 is drawn as a tube in salmon, and the β-motif is indicated.