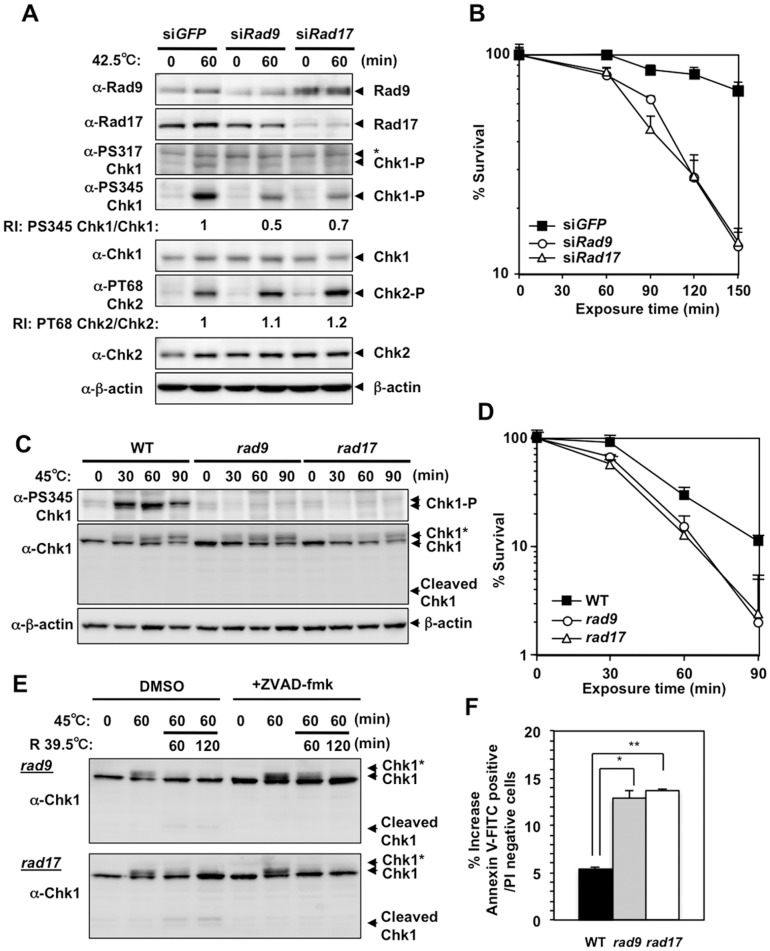
Figure 2. Rad9- or Rad17-deficiency inhibited heat-induced Chk1 phosphorylation at Ser345 and enhanced heat cytotoxicity.
A. Western blot. HeLa cells were transfected with siRNA for GFP, Rad9 or Rad17 and cultured at 42.5°C for 60 minutes. Non-specific bands were indicated as *. RI: relative intensity compared to the sample of siGFP and 42.5°C for 60 minutes. B. Clonogenic survival. HeLa cells were transfected with siRNA for GFP, Rad9 or Rad17 and cultured at 42.5°C for the indicated time. C. Western blot. Wild-type, Rad9- and Rad17-deficient DT40 cells (WT, rad9 or rad17) were cultured at 45°C for the indicated time. D. Clonogenic survival. WT, rad9 and rad17 DT40 cells were cultured at 45°C for the indicated time. E. Western blot. The rad9 and rad17 DT40 cells were cultured at 45°C for 60 minutes and at 39.5°C for the indicated time in the presence of DMSO or caspase inhibitor (50 µM ZVAD-fmk). F. The induction of early apoptotic cells by heat. Early apoptotic cells were detected as annexin V-FITC-positive, propidium iodide (PI)-negative population. WT, rad9 and rad17 DT40 cells were cultured at 45°C for 60 minutes and at 39.5°C for 60 minutes, and the increase in early apoptotic cells induced by these treatment is shown. *p = 0.0016, **p = 0.0002 (Student's t test).