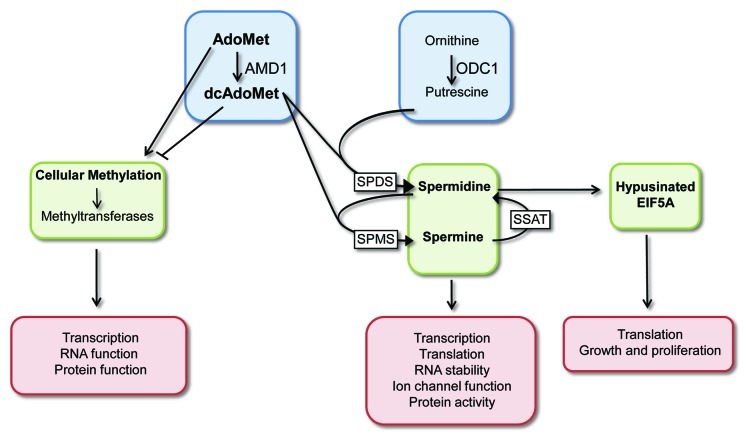
Figure 1. Overview of the polyamine pathway. AMD1 promotes the conversion of AdoMet to dcAdoMet, and the ratio and levels of these feed into three major downstream pathways: high dcAdoMet results in high spermine and spermidine levels, both of which are implicated in regulation of gene expression and protein function. High spermidine levels result in increased levels of hypusinated EIF5A, which can influence translation, growth and proliferation. AdoMet is the methyl donor for DNA methyltransferases in the cell, and high dcAdoMet functions to inhibit methytransferase activity. Methylation impacts on gene expression control at the RNA and DNA levels and the activity of proteins and phospholipids. ODC1 functions to decarboxylate ornithine to produce putrescine, which is required for the synthesis of spermidine and spermine. Abbreviations: SPMS, spermine synthase; SPDS, spermidine synthase; SSAT, spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.