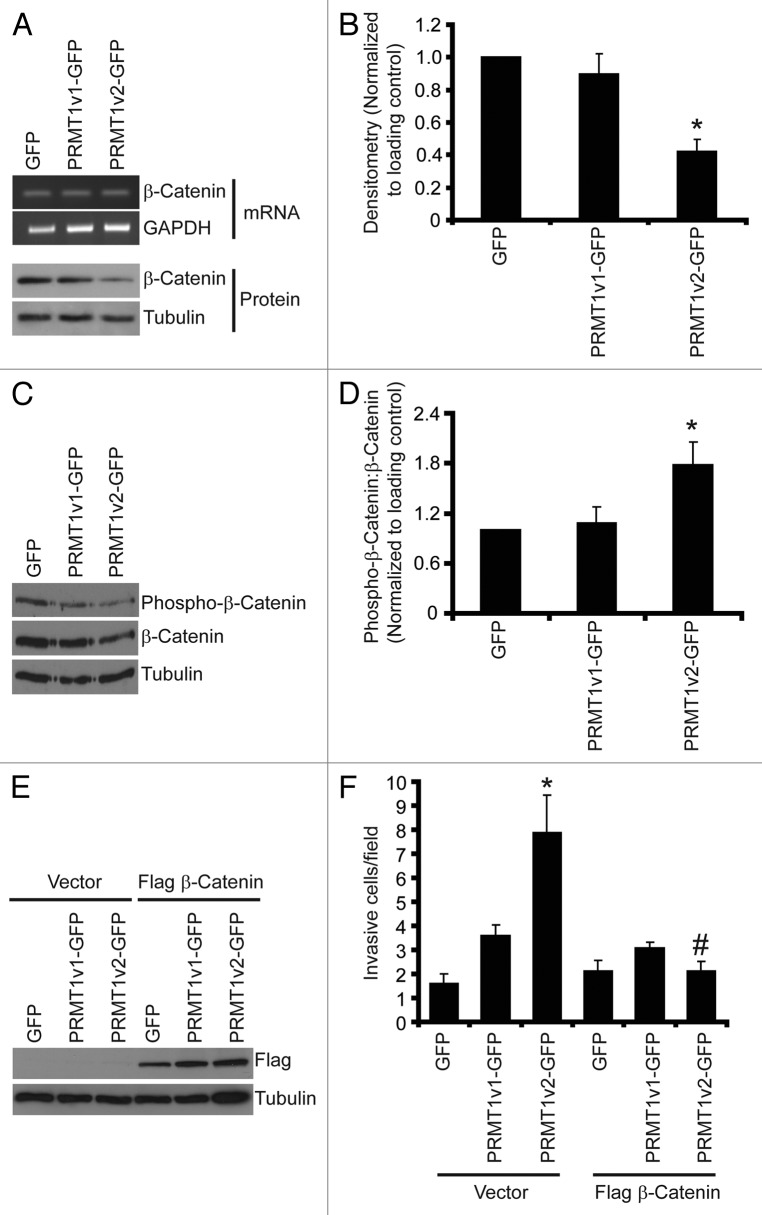
Figure 8. PRMT1v2 expression causes a decrease in β-catenin expression. Total RNA was collected from MCF7 cells stably expressing GFP, PRMT1v1-GFP or PRMT1v2-GFP. PCR analysis of cDNA generated from total RNA using β-catenin primers (A, mRNA). GAPDH serves as a loading control. Total protein lysates collected from MCF7 cells stably expressing GFP, PRMT1v1-GFP or PRMT1v2-GFP and were analyzed by western blotting for the expression of β-catenin protein (A, protein). Tubulin serves as a loading control. Densitometry of β-catenin protein expression normalized to loading control. Values are expressed relative to MCF7 GFP expressing cells (B). Data represents the mean ± standard error of seven independent experiments (*p < 0.01 comparing to GFP or PRMT1v1-GFP). Western blotting for levels of phosphorylated β-catenin using a phospho-specific antibody that recognizes phosphorylation at Ser33, Ser37 and Thr41 as well as total β-catenin and tubulin (C). Densitometry was used to determine the ratio of phosphorylated β-catenin to total β-catenin protein expression normalized to loading control (D). Values are expressed relative to MCF7 GFP-expressing cells. Data represents the mean ± standard error of three independent experiments (*p < 0.05 compared with GFP and PRMT1v1-GFP). MCF7 cells stably expressing GFP, PRMT1v1-GFP or PRMT1v2-GFP were transiently transfected with an expression plasmid containing flag-tagged β-catenin. Western blot analysis for flag 24 h post-transfection (E). Tubulin serves as a loading control. Following 24 h, transfection with flag-tagged β-catenin containing plasmid cells were replated at equal numbers in Transwell chambers containing a Matrigel layer and incubated for an additional 72 h. Cell numbers that passed through the chambers were counted (F). Data represents the mean ± standard error of three independent experiments (*p < 0.05 comparing to control, #p < 0.05 comparing to PRMT1v2 vector control).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.