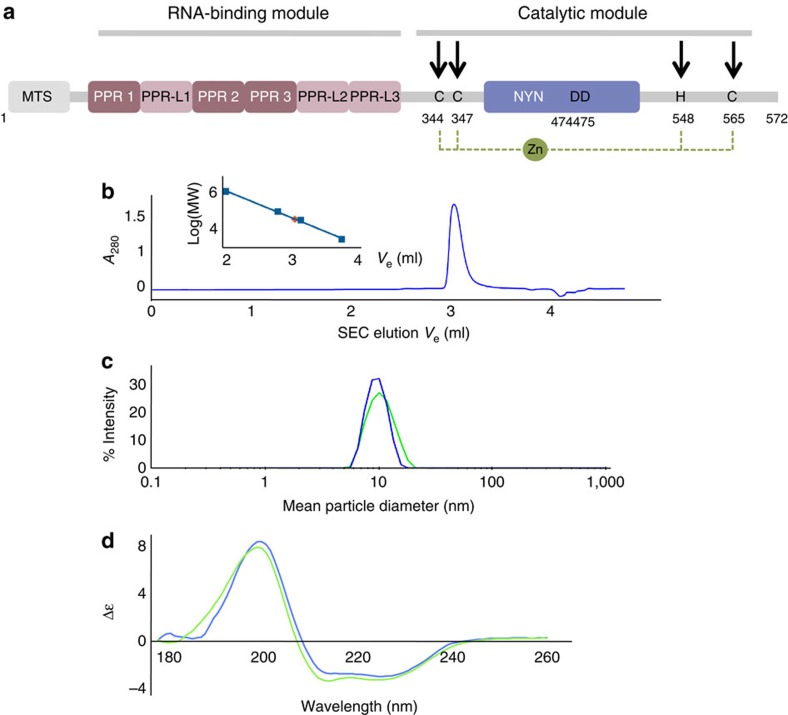
Figure 3. Characterization of PRORP proteins in solution.
(a) Organization along the sequence of PRORP proteins. In the RNA-binding domain PPR and PPR-L show canonical PPR repeats and putative PPR-like motifs, respectively. For PRORP1, aspartates at positions 474 and 475 are in the catalytic pocket of the enzyme9, whereas cysteines and a histidine at positions 344, 347, 548 and 565 (indicated by black arrows) are proposed to form a zinc-binding pocket (dashed line) that could stabilize the catalytic domain of PRORP. (b) Analysis of PRORP2 oligomeric state in solution by analytical gel-filtration (BioSEC3 column) leading to a MW estimation of 72 kDa (red diamond: Log(MW)=4,85) by comparison with the elution of model proteins (thyroglobulin: 660 kDa; BSA monomer and dimer: 66, 132 kDa; ribonuclease A: 14 kDa; see inset). (c) Hydrodynamic radius distribution for PRORP1 (green) and PRORP2 (blue) in dynamic light scattering, confirming the monodispersity of PRORP samples. (d) SRCD analysis of PRORP1 (green) and PRORP2 (blue). SRCD spectra show a dominant peak at 190–200 nm characteristic of α-helices. The evaluation of two-dimentional structure content indicates 36/39% of α-helices, 15/16% of β-strands in PRORP1/PRORP2, respectively.