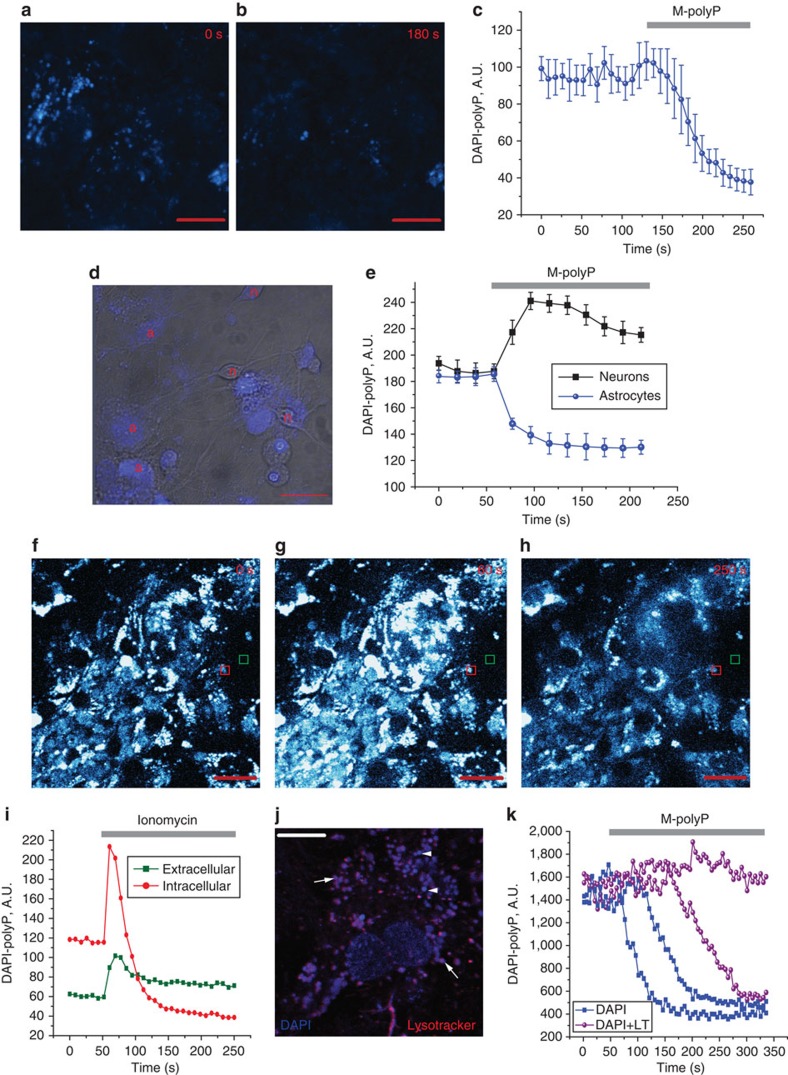
Figure 2. Uptake and release of polyP in primary neuroglial co-cultures.
PolyP can be detected in vesicle-like structures in astrocytes using DAPI (DAPI-polyP) (a). Application of M-polyP (50 μM) to DAPI-loaded neuroglial cultures induces release of polyP as seen by a decrease in intracellular vesicular DAPI-polyP (a–c). Error bars represent s.e.m. n=93 cells. Shown are representative images from two time points and the mean trace. Scale bar, 10 μm. PolyP released from astrocytes (a) upon stimulation with M-polyP (50 μM) is taken up by neurons (n) as seen by DAPI-polyP (d). (d) Bright-field image combined with DAPI-polyP staining (blue). Scale bar, 20 μm. (e) Representative mean traces from neurons and astrocytes. Error bars represent s.e.m. n=54 neurons and n=61 astrocytes. (f–i) Application of ionomycin (5 μM) induces release of vesicular polyP from cortical astrocytes. Shown are representative images from three time points (0, 60, 250 s) (f–h) and the corresponding traces (i). (j) Loading of neuroglial cultures with DAPI and Lysotracker (LT) simultaneously indicates partial colocalization of DAPI-polyP with lysosomes (arrows), whereas other DAPI-polyP vesicles do not stain with LT (arrow heads). Scale bar, 10 μm. (k) PolyP is released from a proportion of LT and DAPI co-stained vesicles upon addition of 50 μM M-polyP.