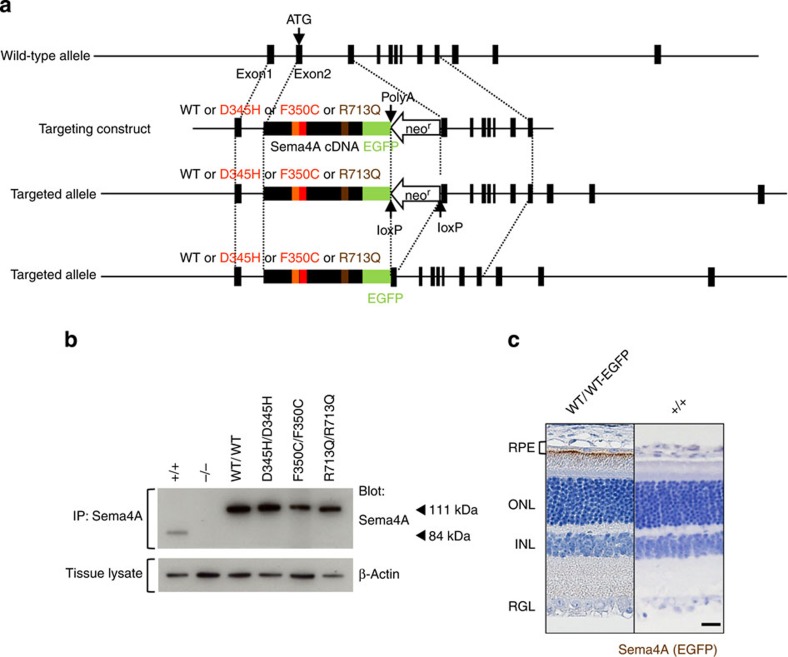
Figure 1. Generation of knock-in mice.
(a) Schematic diagram of the endogenous mouse locus for the Sema4A knock-in vectors and the resulting Sema4A proteins after homologous recombination. Full-length cDNA fragments of WT Sema4A or mutated Sema4A (D345H, F350C or R713Q) fused with EGFP at the C-terminus were inserted into exon 2 and exon 3 of the Sema4A gene. The neomycin resistance gene was flanked by loxP sites so that it could be excised upon expression of Cre recombinase. The gene structure of the WT Sema4A allele (top), Sema4A-targeting construct (second row) and the resulting Sema4A-targeted allele in which the neomycin resistance gene was (bottom) or was not (third row) excised. (b) Expression of Sema4A proteins in the brain tissues of knock-in mice. Brain tissues from WT (Sema4A+/+), Sema4AWT/WT, Sema4AD345H/D345H, Sema4AF350C/F350C, Sema4AR713Q/R713Q and Sema4A−/− (negative control) mice were lysed and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) and Western blot analyses using an anti-Sema4A antibody. The 111-kDa bands represent the mutant Sema4A-EGFP proteins (EGFP-tagged), while the 84-kDa band represents the endogenous wild-type Sema4A protein. All series of knock-in mice expressed sufficient amounts of Sema4A protein. (c) Paraffin sections of Sema4AWT/WT or wild-type (Sema4A+/+) (negative control) retinas were examined by immunohistochemistry with an anti-GFP antibody. Sema4A normally localizes at the apical surface of RPE cells in the retina. Scale bar, 50 μm.