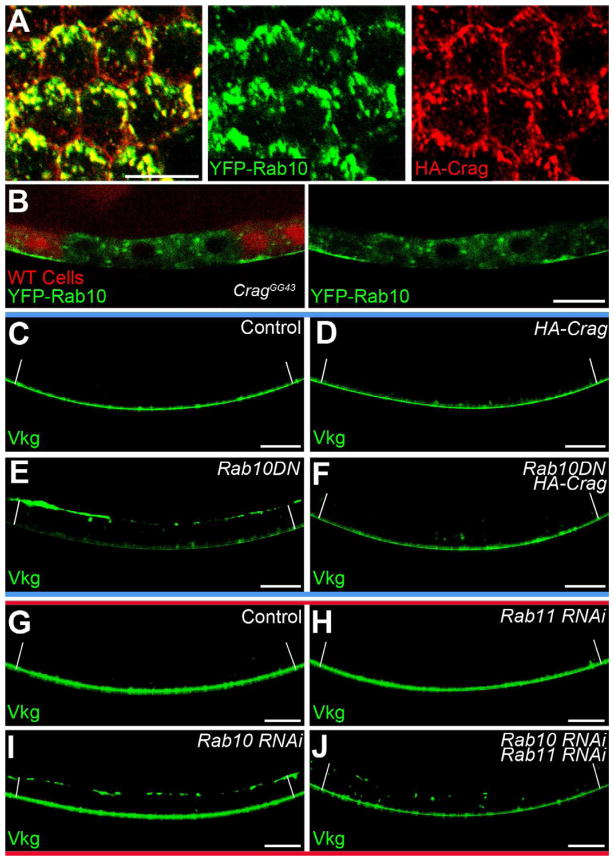
Figure 6. Crag regulates Rab10 during polarized BM secretion.
(A) Optical section near the basal surface showing YFP-Rab10 and HA-Crag co-localization. (B) A CragGG43 follicle cell clone shows a redistribution of YFP-Rab10 away from the basal surface. (C–F) Interaction between UAS-HA-Crag and UAS-Rab10.T23N. (C–D) Vkg-GFP localization is normal in (C) wild-type and (D) UAS-HA-Crag follicle cells. (E) A UAS-Rab10.T23N dominant negative transgene causes Vkg-GFP to accumulate on the apical surface. (F) Co-expression of UAS-HA-Crag with UAS-Rab10.T23N suppresses this phenotype. (E–F) A YFP on Rab10.T23N contributes to the fluorescent signal in the cytoplasm. (G–J) Interaction between Rab10-RNAi and Rab11-RNAi. (G and H) Vkg-GFP localization is normal in (G) wild-type and (H) Rab11-depleted cells. (I) Rab10 depletion causes Vkg-GFP to accumulate on the apical surface. (J) Co-depletion of Rab10 and Rab11 eliminates the apical Vkg-GFP and increases the cytoplasmic signal. (C–J) White lines extend between the apical and basal epithelial surfaces. Experiments performed at stages 7–8. Scale bars are 10 μm. See also Figure S6.