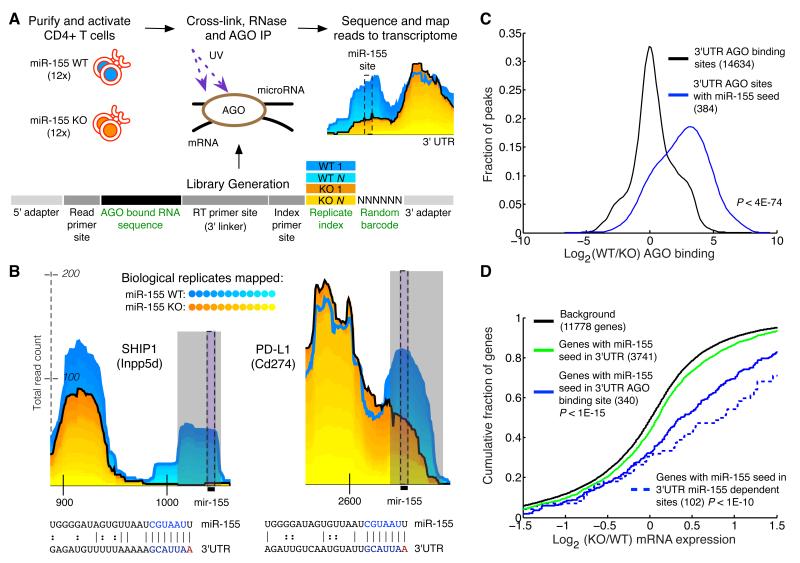
Figure 1. Differential CLIP-sequencing identifies sites of miR-155 mediated Argonaute binding.
(a) CD4+ T cells were isolated from miR-155-sufficient and - deficient mice and RNase treated cell lysates were subjected to Argonaute (AGO) immunoprecipitation. Following stringent purification of complexes, indexed and barcoded libraries were prepared and subjected to Illumina high-throughput sequencing. (b) Examples of AGO binding sites in novel (PD-L1) and established (SHIP1) canonical targets. Grey rectangles indicate miR-155-dependent binding sites (p < .01) called by edge detection method. Reads from the 12 replicates have been stacked; blue shades are miR-155-sufficient (WT) replicates, and yellow shades are mir-155-deficient (155KO) replicates. Black bars indicate the location of the miR-155 seed in the binding site. Coordinates along the x-axis indicate nucleotide position relative to the beginning of the 3′UTR. The y-axis indicates read counts, which are square root transformed following individual library normalization (see Computational Methods). (c) Relative AGO binding in WT and 155KO cells at all 3′UTR binding sites, or 3′UTR binding sites containing a miR-155 seed. (d) Gene expression differences assessed by microarray between WT and 155KO cells of targets predicted by seed, AGO binding sites, or miR-155 dependent AGO binding sites. p-values were calculated by using a one-sided KS test.