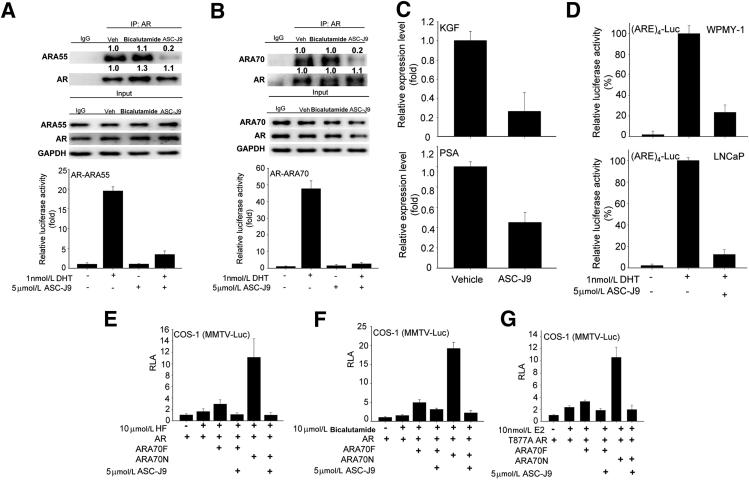
Figure 1.
ASC-J9 selectively promotes AR degradation via interrupting the interaction between AR and AR coregulators. A: ASC-J9 disrupted the interaction between AR and ARA55 in WPMY-1 cells. Top and middle panels: Co-IP assay of the AR-ARA55 complex in WPMY-1 cells examined by immunoblotting assay. The 5 μmol/L proteasome inhibitor MG-132 was added for 30 minutes before adding the vehicle (Veh), 5 μmol/L bicalutamide, or 5 μmol/L ASC-J9 to prevent protein degradation. The quantitation data of Co-IP are presented as fold increase compared with the Veh group by densitometric analysis of bands. The input loading controls show similar amounts. Bottom panel: The mammalian two-hybrid assay was used to demonstrate that 5 μmol/L ASC-J9 can suppress the interaction between AR and ARA55. B: ASC-J9, 5 μmol/L, dissociated the binding of AR and ARA70 in LNCaP cells. Top and middle panels: Co-IP of AR-ARA70 complex in LNCaP cells, with or without ASC-J9 treatment, and determined by immunoblotting assay. MG-132 at 5 μmol/L was added before treatment. The quantitation of Co-IP results are presented as fold increase compared with the Veh group. Bottom panel: ASC-J9 also showed the inhibitory effects on the interaction between AR-ARA70 by mammalian two-hybrid assay. C: The reduction of keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) mRNA levels in WPMY-1 cells (top panel) and PSA levels in LNCaP cells (bottom panel) after 5-μmol/L ASC-J9 treatments. D: ASC-J9, 5 μmol/L, treatment reduced (ARE)4-luciferase (Luc) activity in WPMY-1 (top panel) and LNCaP cells (bottom panel) after DHT stimulation. E–G: ASC-J9 suppressed ARA70-mediated AR transcriptional activity in COS-1 cells after HF, bicalutamide, or 17β-estradiol (E2) treatment using MMTV-Luc reporter assay. ARA70 full-length (ARA70F), ARA70 N-terminal amino acid 1-401 (ARA70N), and mutant AR (T877A AR) are shown. Error bars = mean ± SD. RLA, relative luciferase activity.