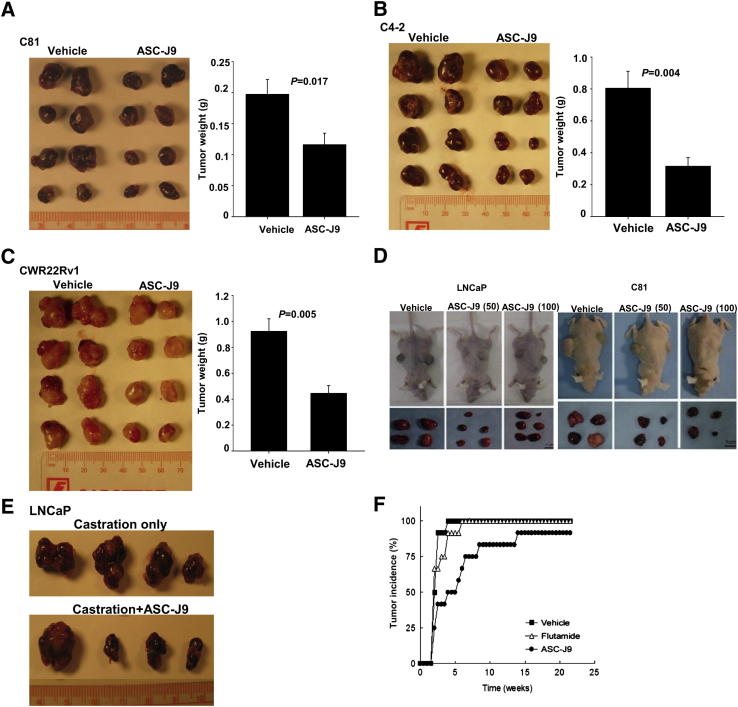
Figure 5.
The in vivo antitumor and chemopreventive effects of ASC-J9 in the xenograft mouse PCa model. A: ASC-J9 suppressed C81 xenografted tumor growth in castrated nude mice. C81 cells were orthotopically implanted into anterior prostates of castrated nude mice and grown for 3 to 4 weeks. Mice were then treated with vehicle or 75 mg/kg of ASC-J9 every other day. The tumors were harvested after 3 weeks of treatment. The representative gross appearances of eight tumors from five to six mice per group (left panel) and the quantitation data of tumor weights (right panel) are shown. B: ASC-J9 inhibited tumor growth of C4-2 xenograft in castrated nude mice. C: ASC-J9 inhibited CWR22Rv1 xenografted tumor growth in castrated nude mice. D: ASC-J9 suppressed androgen-sensitive LNCaP (left panel) and androgen-insensitive C81 (right panel) xenografted tumor growth in intact nude mice. The 50 or 100 mg/kg of ASC-J9 was administered twice per week starting 2 to 3 weeks after s.c. implantation. The gross appearance of LNCaP and C81 xenografted nude mice (top panels) and the dissected prostate tumors (bottom panels) are shown. Scale bars: 200 μm (original magnification, ×100) and 50 μm (original magnification, ×400) E: ASC-J9 suppressed castration-resistant LNCaP xenografted tumor growth in vivo. LNCaP cells were orthotopically implanted into anterior prostates of intact nude mice and were grown for 25 to 28 days. Mice were then castrated, and ASC-J9 treatment was started 5 days after castration. The tumors were harvested after 2 weeks of treatment. N = 4 mice per group. F: ASC-J9 treatment shows significant delayed tumor incidence compared with the vehicle- and flutamide-treated groups. The ASC-J9 was injected or a flutamide pellet was implanted into 4-week-old nude mice when LNCaP cells were s.c. injected into the flanks. The palpable tumor formation was checked weekly.