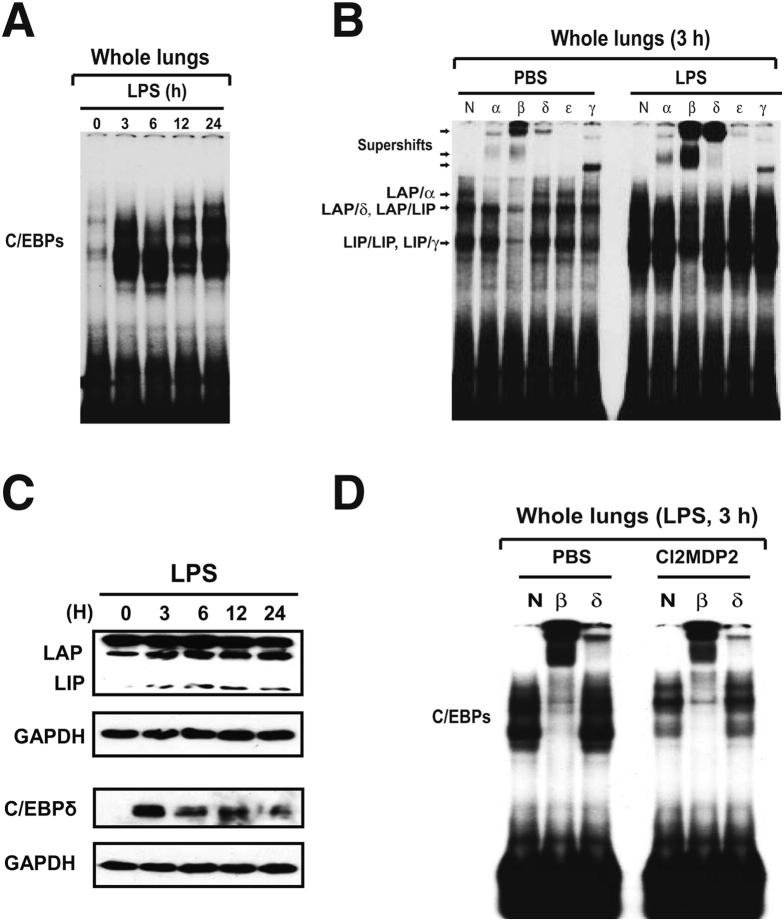
Figure 1.
Lung C/EBP activation during LPS-induced alveolitis. A: Time course for C/EBP activation in LPS-injured lungs. Nuclear extracts from whole lung tissues were subjected to EMSA analysis using a labeled canonical C/EBP site probe. B: Nuclear proteins extracted from whole lung at 0 and 3 hours after LPS deposition were subjected to supershift. The following antibodies were used: normal rabbit IgG (N), anti-C/EBPα antibody (α), anti-C/EBPβ antibody (β), anti-C/EBPδ antibody (δ), anti-C/EBPε antibody (ε), and anti-C/EBPγ antibody (γ). Supershifted species and C/EBP dimers are indicated. C: Western blot analysis of C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ during LPS-induced lung injury. D: Effects of alveolar macrophage depletion on C/EBP activation during LPS-induced lung injury. Mice received PBS-liposome or Cl2MDP-liposomes 24 hours before intratracheal challenge with either PBS or LPS. At 3 hours after PBS or LPS challenge, lungs were harvested. C/EBP binding activity in whole lung nuclear extracts was assessed by EMSA. LAP, liver-enriched activator protein; LIP, liver-enriched inhibitory protein.