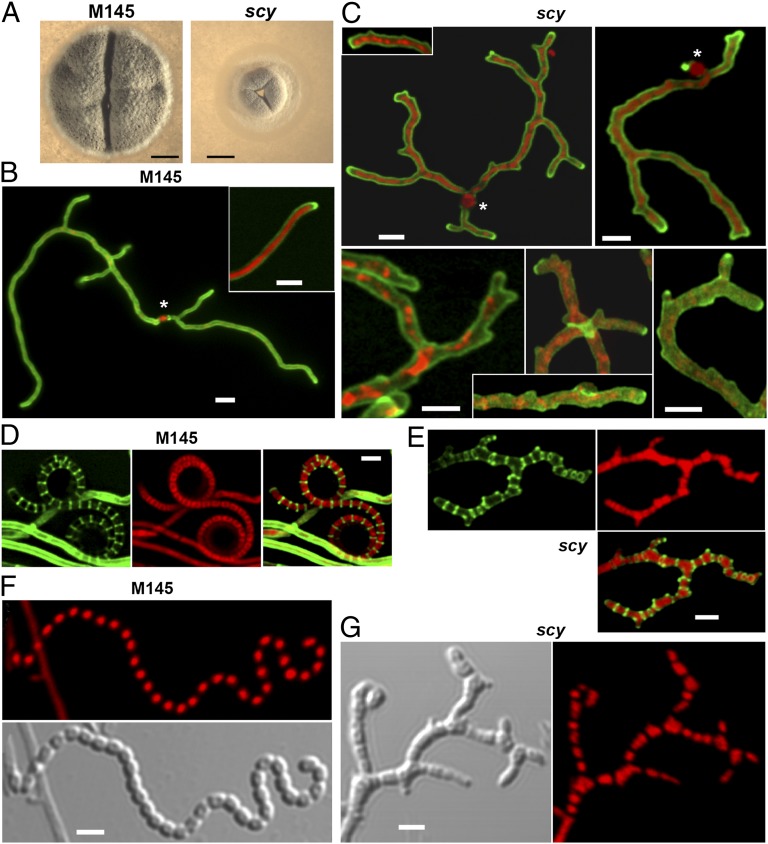
Fig. 2.
Mutation of scy severely affects polarized growth and development. (A) Single colonies of S. coelicolor M145 (WT) and K110 (scy mutant) are shown after 6 d of growth. To ensure that colony density did not affect growth, we plated a similar number of colonies, ∼100 cfu per plate. (Scale bars: 1 mm.) The WT (B) and the scy mutant, K110 (C), were grown for 16 h, and the branching hyphae originating from single spores (marked with asterisks) were viewed using laser-scanning confocal microscopy after staining the cell wall with WGA-Alexa488 (green) and the chromosomes with propidium iodide (PI; red). Overlaid images of the two fluorescent channels are shown (see also Fig. S2). Early spore chains of the WT (D) and the scy mutant, K110 (E), were stained as above after growth for 44 h alongside microscope coverslips to allow viewing of aerial development and sporulation. Images of the two fluorescent channels are shown separately in addition to the overlaid view. Mature spore chains of the WT (F) and the scy mutant, K110 (G), were stained with PI (red) after growth for 72 h as in D and E. A differential interference contrast image is also shown. (Scale bars: B–G, 1 μm.)