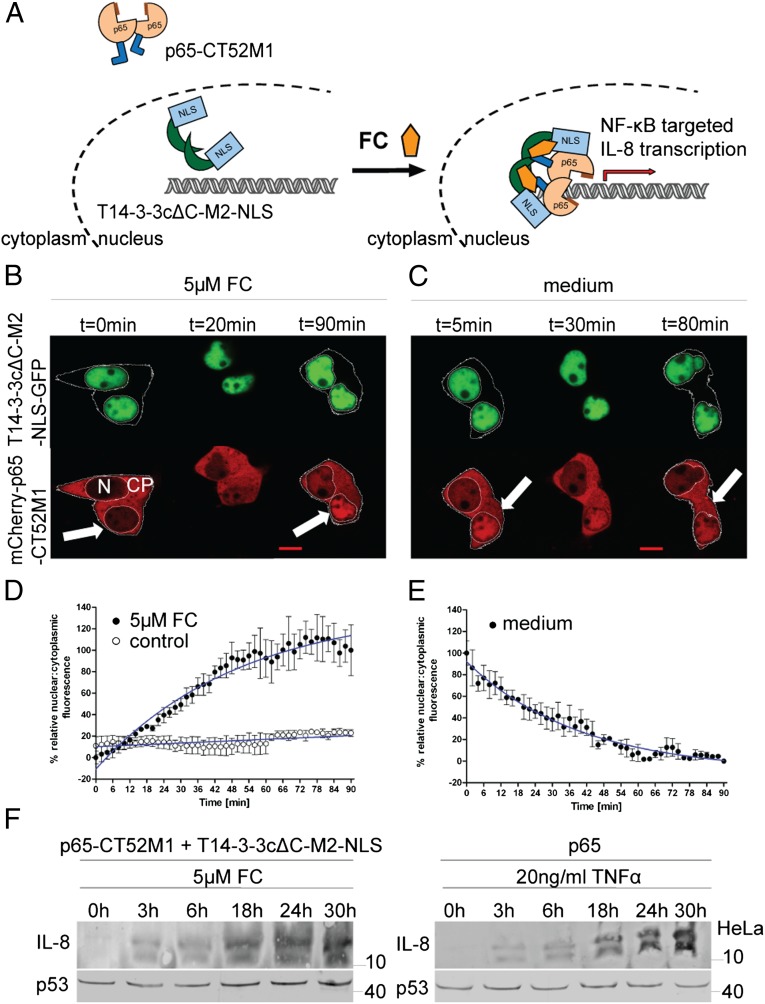
Fig. 5.
FC-induced nuclear accumulation of NF-κB (p65). (A) Schematic representation of FC-induced nuclear accumulation of p65-CT52M1. (B and C) Time-course images of HEK293T cells transfected with plasmids encoding for T14-3-3cΔC-M2-NLS-GFP and mCherry-p65-CT52M1 at stated times, monitoring nuclear accumulation of mCherry-p65-CT52M1 fluorescence after the addition of 5 µM FC (B) and its reverse translocation after the cells were washed with medium (C). See SI Appendix, Fig. S6D for control cells treated with solvent (3.3% ethanol). (Scale bars, 10 μm.) CP, cytoplasm; N, nucleus. (D and E) Quantification of mCherry-p65-CT52M1 translocation in response to 5 µM FC and the analysis of untreated cells (control) (D) and of the reversibility of mCherry-p65-CT52M1 translocation (E). Mean nuclear and cytoplasmic fluorescent intensities were analyzed as described in Fig. 4 E and F. (F) Induction of IL-8 expression by FC in HeLa cells cotransfected with plasmids encoding for T14-3-3cΔC-M2-NLS and p65-CT52M1 demonstrated by Western blotting. Secreted IL-8 was detected upon treatment with 5 µM FC during a time course of 30 h (Left). For a positive control, p65-transfected HeLa cells were treated with 20 ng/mL TNF-α for the same time course (Right). Endogenous p53 was used as a loading control.