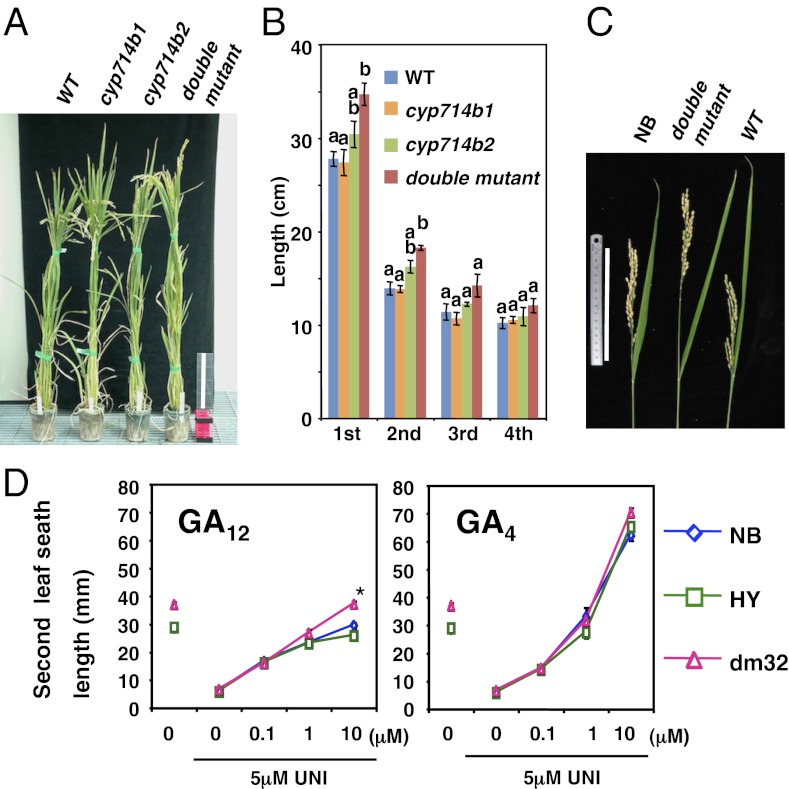
Fig. 5.
Phenotypes of cyp714b1 cyp714b2 double mutant plants. (A) Twenty-two-week-old plants of F2 WT, cyp714b1, and cyp714b2 single and the double mutant. (Scale bar, 20 cm.) (B) Internode length of F3 WT (line 57), cyp714b1 (line 1), cyp714b2 (line 4), and the double mutant (line 32). Mean ± SEM, n = 5–6. Letters above bars indicate statistically significant differences between samples by one-way ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison test (P < 0.01). (C) Panicle exertion (heading performance) of Nipponbare (NB), double mutant, and F3 WT. (Scale bar, 15 cm.) (D) Response to exogenous GA12 or GA4. WTs (NB and HY) and double mutants (F5 line 32) grown on half-strength Murashige-Skoog medium containing various concentrations of GAs and/or uniconazole (UNI). Mean ± SEM, n = 6–11. *Significant difference between dm32 and WTs (Student t test with Bonferroni corrections, P < 0.001).