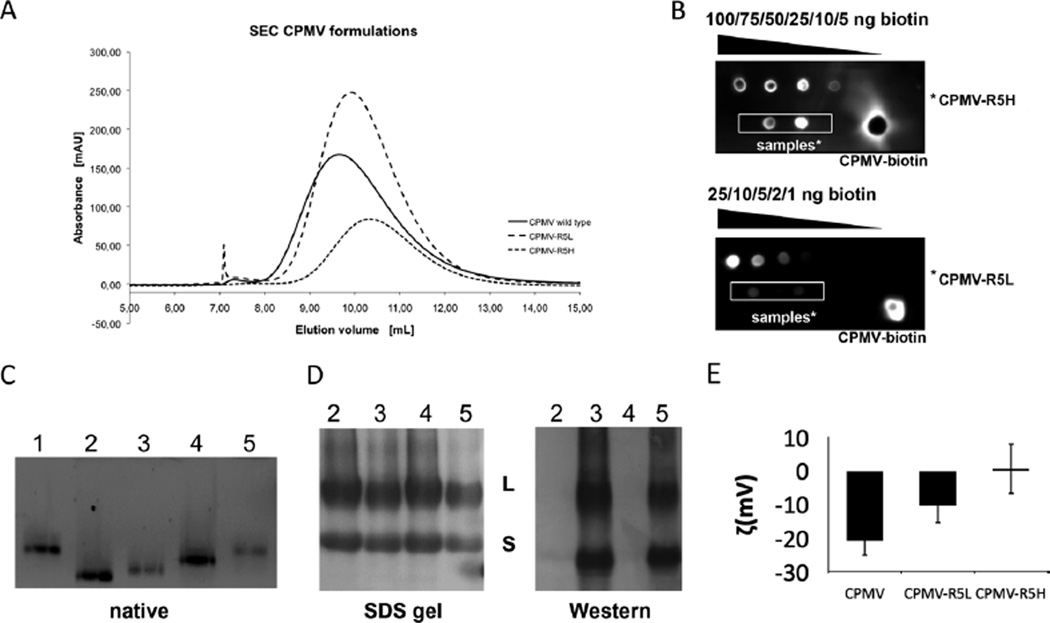
Fig. 2.
Characterization of CPMV labeling with the biotinylated R5 peptide. (A) Size exclusion chromatography of wild-type CPMV, CPMV–R5L and CPMV–R5Hat 280 nm. (B) ECL dot blot of purified CPMV particles. The number of biotin labels per particle was determined using standardized biotin concentrations and Chemidoc XRS software. (C) Native gel electrophoresis of intact CPMV particles (10 µg) using a 0.8% (w/v) agarose gel. Particles were visualized under UV light. Lane 1 = CPMV, 2 = CPMV–4FB, 3 = CPMV–R5H, 4 = CPMV–PFB, 5 = CPMV–R5L. (D) SDS–PAGE of CPMV particles (10 µg) using a 4–12% Bis-Tris gel and western blotting using streptavidin–alkaline phosphatase to detect the N-terminal biotin tag of the R5 peptide. (E) Zeta potential of CPMV wild type, CPMV–R5L and CPMV–R5H formulations.