Fig 4.
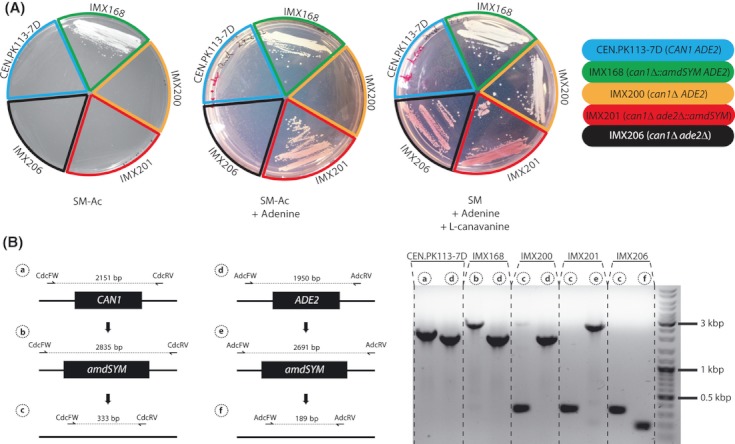
Sequential gene deletions of CAN1 and ADE2 using amdSYM in S. cerevisiae. (A) The strains IMX168, IMX200, and IMX201 and the parental strain CEN.PK113-7D were grown on SM-Ac, SM-Ac supplemented with adenine, and SM supplemented with adenine and l-canavanine. The plates were incubated at 30 °C and were read after 3 days. (B) PCR analysis to confirm correct integration of the gene disruption cassettes and their removal at the CAN1 and ADE2 loci. PCR was carried out on reference CEN.PK113-7D, IMX168, IMX200, and IMX201. All PCRs were performed with the primer pairs CdcFW/CdcRV and AdcFW/AdcRV for CAN1 and ADE2 loci, respectively. In the parental strain, amplification of the CAN1 and ADE2 loci generated fragments of 2151 bp (a) and 1950 bp (d) for CAN1 and ADE2, respectively. PCR on IMX168 DNA generated a fragment of 2835 bp (b) due to the incorporation of amdSYM in the CAN1 locus. A short fragment of 333 bp (c) was obtained for IMX200 as a result of amdSYM excision from the CAN1 locus. Similarly, the disruption of ADE2 using amdSYM led to a large PCR product of 2691 bp in IMX201 (e) while PCR on the ADE2 locus in the marker-free strain IMX206 generated a short fragment of 189 bp (f). The products obtained were then subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis.
