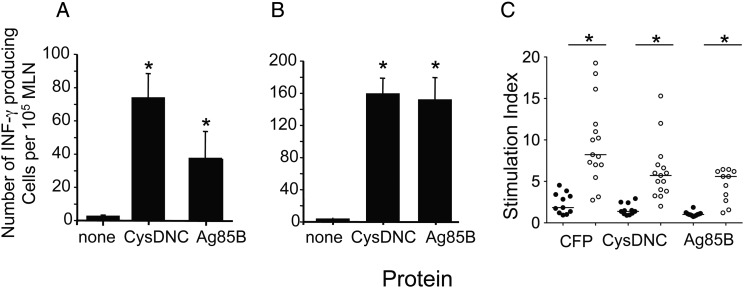
Figure 2.
Host immune recognition of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis sulfate-activation complex. Antigen-specific T-cell responses in the mediastinal lymph node (MLN) of mice were measured 3 (A) and 8 (B) weeks following intranasal M. tuberculosis challenge. Interferon γ (IFN-γ)–secreting cells were enumerated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot following stimulation with CysDNC or 85B proteins (10 μg/mL). Data are the means ± standard error of the mean for 4 mice and are representative of duplicate experiments. The significance of differences between protein-stimulated and unstimulated cells was determined by analysis of variance; *P <.0001. C, Antigen-specific T-cell responses were measured in the peripheral blood of M. tuberculosis–infected patients (open circles; n = 15) and tuberculin skin test–negative individuals (filled circles; n = 11). T-cell proliferation in response to M. tuberculosis CFP, CysDNC, and Ag85B proteins at 10 μg/mL was measured via the incorporation of 3H-thymidine, and a stimulation index was calculated. Horizontal lines represent the median for each group. Significance of differences between M. tuberculosis–infected patients and TST-negative individuals was determined by the Mann–Whitney U test; *P < .001.