Fig.4. A sustained T cells stimulation enhance to form CD69 nano-domains with peak- polarity or CD71 nano-domains with valley-polarity in number and molecule density on the cell membrane fluctuations.
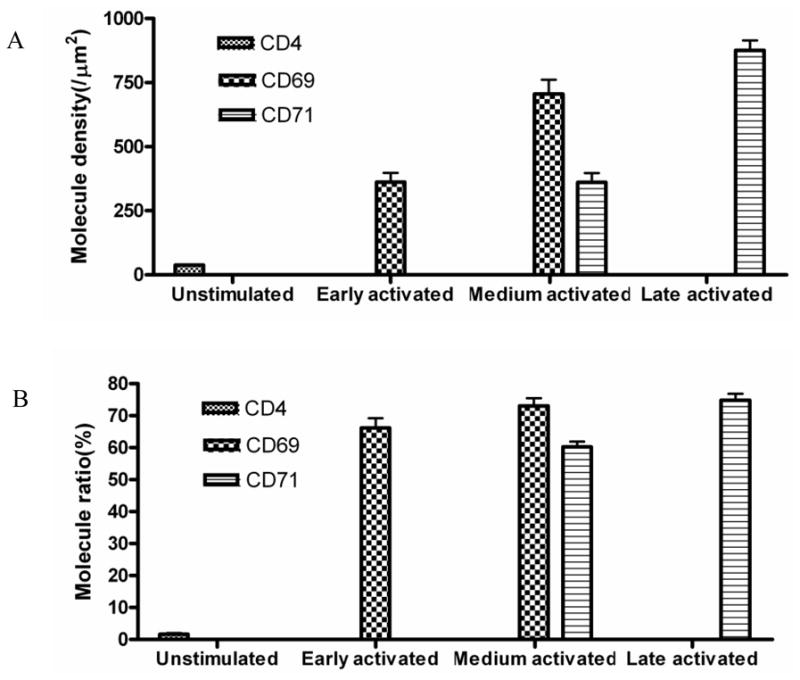
(A) Molecular-density analysis showed the molecular density of CD4 molecules on the membrane of un-stimulated T cells, molecular density of CD69 or CD71 molecules of early-term, medium-term, late-term activated T cells. Activated T cells exhibited significantly greater molecule density of CD69 or CD71 nano-domains compared to molecular density of CD4 of unstimulated T cells(p<0.05); A sustained stimulation significantly increases density of CD69 nano-domains of medium-term activated T cells compared to early-term activated T cells(p<0.05). Similarly, A sustained stimulation significantly increases molecule density of CD71 nano-domains of late-term activated T cells compared to medium-term activated T cells(p<0.05). Up to 10 cells were analyzed. (B)The percentage numbers of CD69 or CD71 molecules that arrayed to form nano-domains significantly increases in medium-term or late-term activated T cells compared to early-term or medium-term activated T cells(p<0.05). Up to 10 cells were analyzed.
