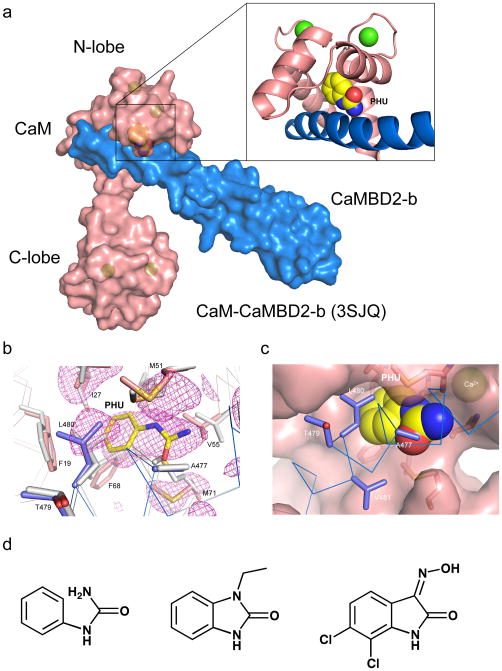
Figure 1. Phenylurea binds to the CaM-CaMBD interface at the CaM N-lobe.
(a) A space-filled model of the CaM-CaMBD2-b complex (3SJQ), depicting the location of PHU (yellow) between the interface of CaM (salmon) and CaMBD2-b (marine) at the CaM N-lobe. Only half of the 2×2 complex is shown for clarity. (b) Difference Fourier electron density map constructed using mFo–DFc coefficients calculated in PHENIX prior to modeling PHU and side chain rearrangements that occur in the binding site. The map is contoured at 2.5σ and displayed within a 6 Å sphere of PHU. The map is overlaid with the final coordinates for PHU and its surrounding amino acid residues in the CaM-CaMBD2-a complex. Marine are amino acid residues from CaMBD2-a and salmon are amino acid residues from CaM. Coordinates of the same amino acid residues (gray) from the original CaM-CaMBD2-a complex (without PHU, 1G4Y) are provided for comparison. (c) A space-filled model of PHU at the CaM-CaMBD interface. Marine represents CaMBD and salmon represents CaM. (d) Comparison of the chemical structure of PHU with that of 1-EBIO and NS309. Both 1-EBIO and NS309 are known SK/IK channel modulators.