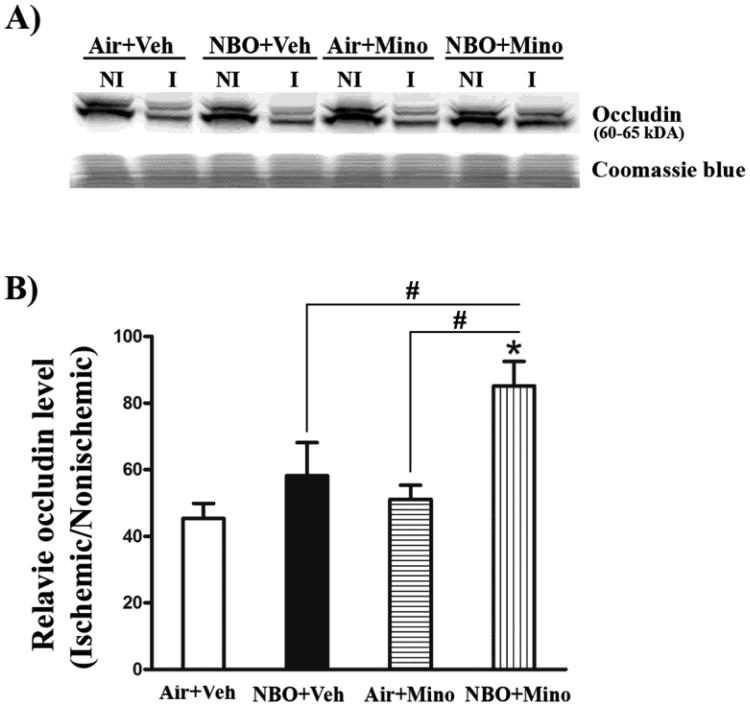
Fig. 4.
Effects of NBO, minocycline and their combination on occludin degradation in the ischemic brain after 90-min MCAO and 48 hrs of reperfusion. Western blot was conducted to detect occludin protein in the nonischemic (NI) and ischemic (I) hemispheric tissue. Veh: vehicle; Mino: minocycline. (A) A representative western blot revealed occludin protein a doublet of 60 and 65 kDa (upper panel). The same membrane was stained with Coomassie blue as a loading control (lower panel). (B) The band intensity of occludin protein was quantitated after normalization to the total protein reflected by Coomassie staining and expressed as hemispheric ratio (ischemic/nonischemic). Cerebral ischemia and reperfusion led to a 55% reduction in occludin protein in the ischemic tissue. The combination therapy significantly inhibited occludin reduction in the ischemic tissue (*P < 0.05 versus Air+Veh), while no significant effect was observed for NBO or minocycline alone. All three treatments did not affect occludin protein levels in the nonischemic hemisphere. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 8 for each group.