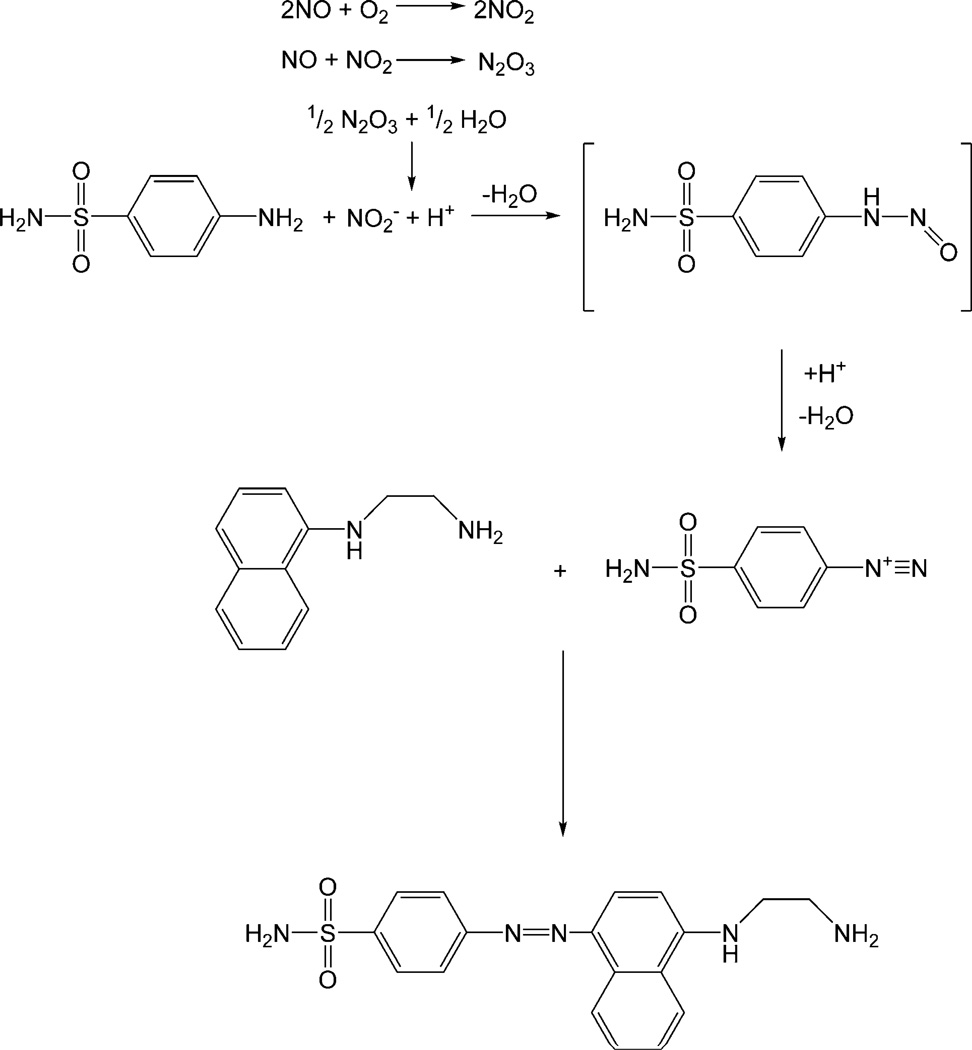
Figure 1.
The most commonly employed diazotization reaction (Griess assay). Under aerobic conditions nitric oxide (NO) reacts to form nitrite (NO2−), which reacts with sulfanilic acid to form a diazonium salt intermediate. The diazonium salt is then coupled to N-(1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine to form the stable water-soluble azo dye (λmax ≈ 540 nm).