Fig. 1. Chronic HFD feeding results in global mitochondrial hyperacetylation and reduces hepatic SIRT3.
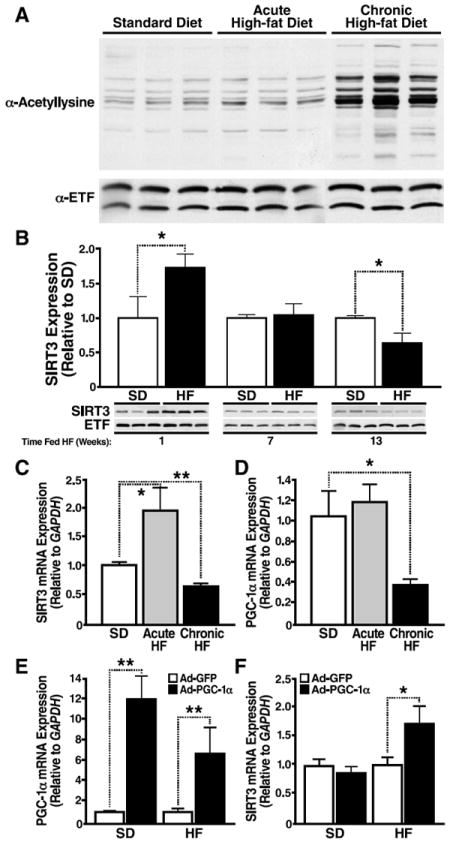
(A) Mitochondria were isolated from livers of wt mice fed a standard or HFD for 1 week or 13 weeks (Jackson Laboratory) and analyzed for mitochondrial protein acetylation by western blot analysis with an antiserum specific anti-acetyllysine; n=3 mice/condition. (B) Mitochondria were isolated from livers of wt mice fed a standard or HFD for 1 week, 5 weeks or 13 weeks (Jackson Laboratory) and analyzed for SIRT3 expression by western blot analysis with an antiserum specific for SIRT3. Integrated density values were calculated for SD and HFD fed wt mice; data represented in arbitrary units (AU) ±SEM, n=3 mice/condition, *p<0.05; (C, D) mRNA transcript levels were quantified by qPCR from wt mice, (from panel B, *p<0.05, n=3/genotype, standard or HFD, ±SEM). (E, F) mRNA transcript levels were quantified by qPCR from wt mice fed a standard (SD) or high-fat (HF) diet overexpressing adenoviral PGC-1α or GFP as a control, (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, n=5/condition, ±SEM).
