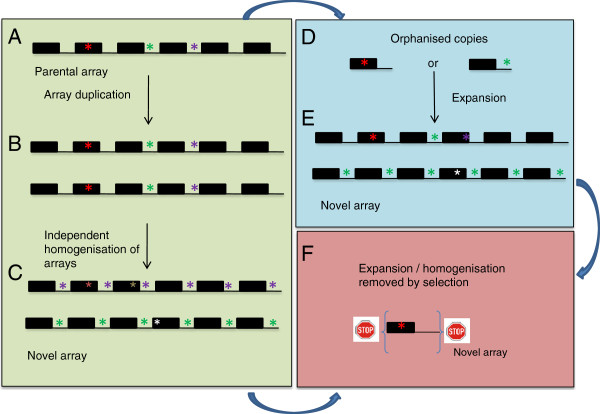
Figure 7.
A theoretical model to explain rDNA divergence. Ribosomal DNA arrays (black box) separated by spacer sequences (black line) with some units carrying mutations (asterisks). Green panel: (A) 35S rDNA locus comprising rDNA arrays with a few mutations. (B) Duplication of the 35S rDNA locus, followed by (C) more rapid intrachromosomal homogenisation than interchromosomal homogenisation, leading to genetic divergence of both arrays and an increase in rDNA complexity. Mechanism would involve unequal recombination and gene conversion [2,69]. Blue panel: (D) Orphaned 35S rDNA copies may (E) nucleate locus expansion, resulting in long arrays of homogenous sequences. Pink panel: (F) Amplification of non-functional units will be selected against and lost from the population partially corroborating birth-and-death model of rDNA evolution [7,8].