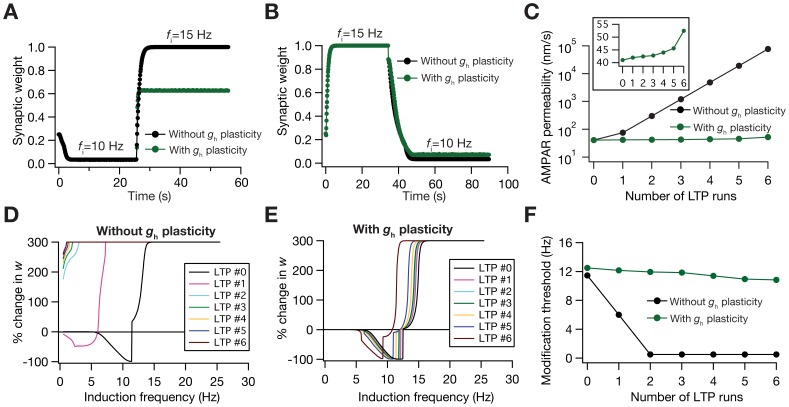
Figure 5. Calcium-dependent plasticity in HCN channels retains dynamic range of the synapses in the face of synaptic plasticity.
(A) Experiment assessing the role of abrupt change in activity on synaptic weight dynamics, with initial induction frequency set at 10 Hz, and switched to 15 Hz after weight reached stable equilibrium with the 10 Hz stimulus. Traces show the cases where synaptic plasticity was accompanied (green) and not accompanied (black) by CDPR. (B) Same as (A), but with the initial and the switch frequencies reversed. (C) Impact of repeated LTP (15 Hz/900 pulses, each induction) on AMPAR permeability depicted as a function of the number of LTP inductions, plotted for cases where synaptic plasticity was accompanied (green) and not accompanied (black) by CDPR. Inset shows the same green plot on a linear scale. (D–E) Effect of repeated LTP on the BCM-like synaptic plasticity profile, plotted for cases where synaptic plasticity was not accompanied (D) and accompanied (E) by CDPR. (F) Modification threshold, calculated from traces shown in (D) and (E), plotted as a function of the number of LTP inductions for cases where synaptic plasticity was accompanied (green) and not accompanied (black) by CDPR. 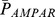 = 41 nm/s and baseline
= 41 nm/s and baseline 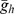 = 0.45 mS/cm2.
= 0.45 mS/cm2.