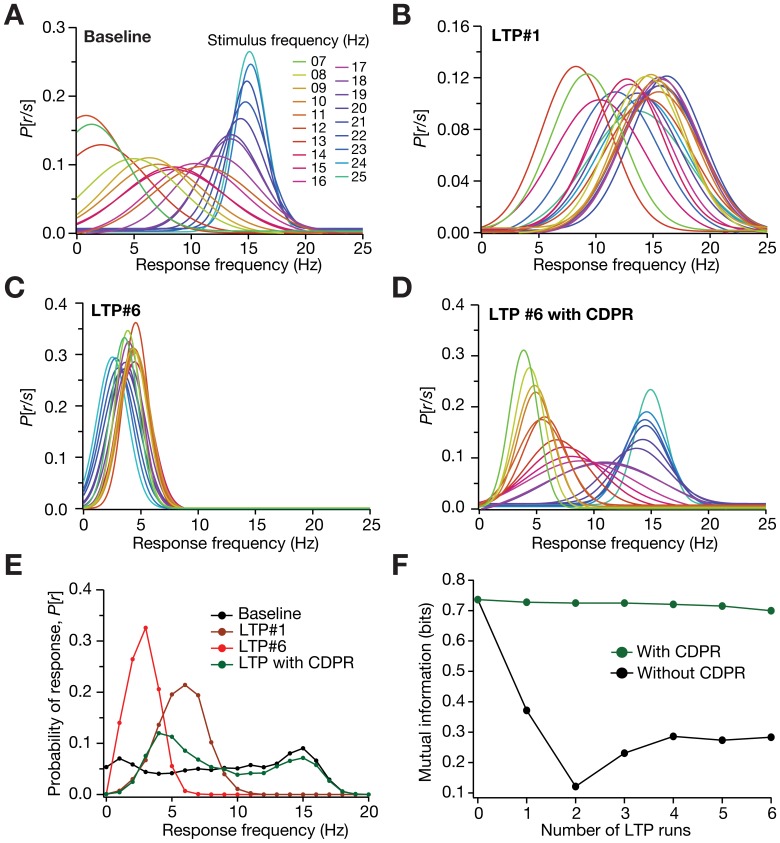
Figure 6. Information transfer across the neuron was more robust when synaptic plasticity was accompanied by HCN channel plasticity.
(A) Probability distribution of response firing frequency, given SF, P [r|s], with baseline parameters. (B–C) P [r|s] after induction of LTP (B; 15 Hz/900 pulses), and after six consecutive LTP inductions (C; 15 Hz/900 pulses, each induction). Synaptic plasticity was not accompanied by CDPR for both cases. (D) P [r|s] after six successive LTP inductions, with CDPR induced in parallel with synaptic plasticity. For P [r|s] depicted in panels (A–D), the individual normal distributions were constructed from the first and second order statistics of the FFs, across trials, for a given SF. (E) Probability distribution for different response frequencies, P [r], plotted for baseline condition (black), after a single run of LTP induction (brown), and after six consecutive LTP inductions accompanied (green) and not accompanied (red) by CDPR. (F) Mutual information plotted as a function of number of successive LTP runs, under cases where CDPR accompanied (green) or did not accompany (black) synaptic plasticity. 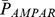 = 41 nm/s and baseline
= 41 nm/s and baseline 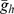 = 0.45 mS/cm2.
= 0.45 mS/cm2.