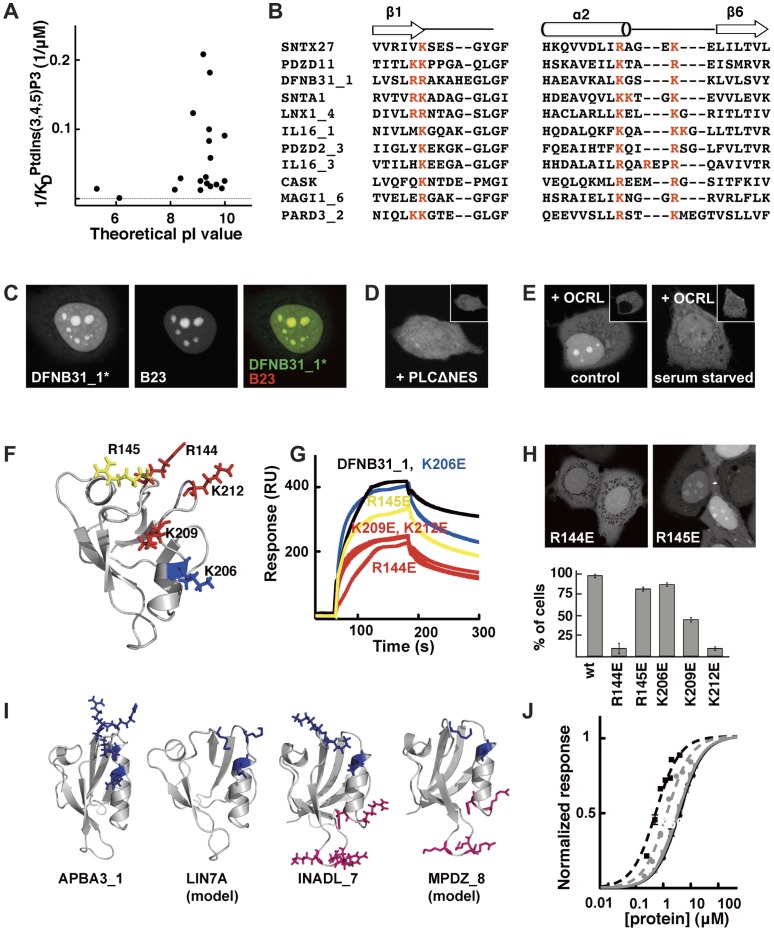
Figure 5. Common features of PtdInsPs interacting PDZ domains.
A. Apparent affinities of individual PDZ domains for PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 (Table S2) plotted versus their theoretical pI values. B. Partial sequence alignment highlighting the conserved positive charge cluster (red letters) shared by eleven PtdInsPs-interacting PDZ domains. C. Confocal micrographs showing the co-localization of eYFP-DFNB31_1* (absence of the S1PDZ1 enhancer) with the nucleolar marker B23. Nucleolar enrichment of eYFP-DFNB31_1* relies on PtdInsPs as co-expression with mCherry-PLCΔNES (D) or serum mediated translocation of mCherry-OCRL (E) shifts expression of eYFP-DFNB31_1* towards the nucleoplasm and the cytoplasm. F. Mutagenic analysis of DFNB31_1. Residues probed by site-directed mutagenesis are indicated in the structure (1UEZ) and were colored according to their effects on PtdIns(4,5)P2 binding: blue, no significant effect; yellow, intermediate effect; red, strong effect. G. Representative double reference subtracted sensorgrams of wild-type and mutant DFNB31_1 proteins (4 µM) injected over 5% PtdIns(4,5)P2-containing DOPC liposomes. The effects of the mutations on the nucleolar enrichment of DFNB31_1 are shown in H. The bar graph illustrates the percentage of transfected cells where strong nucleolar enrichment was observed in confocal microscopy. I. Structures of PDZ domains (APBA31_1, 2YT7; LIN7A, swiss model; INADL_7, 2DAZ; and MPDZ_8, swiss model) having theoretical pI values higher than 7 and defined positive charge clusters (blue and pink stick representations) suggesting potential PtdInsPs-interaction. J. Normalized equilibrium binding isotherms of APBA31_1 (black squares and black dotted line), LIN7A (grey circles and grey dotted line), INADL_7 (black circles and black line) and MPDZ_8 (grey squares and grey line) to 5% PtdIns(4,5)P2 in DOPC liposomes as determined by SPR experiments.