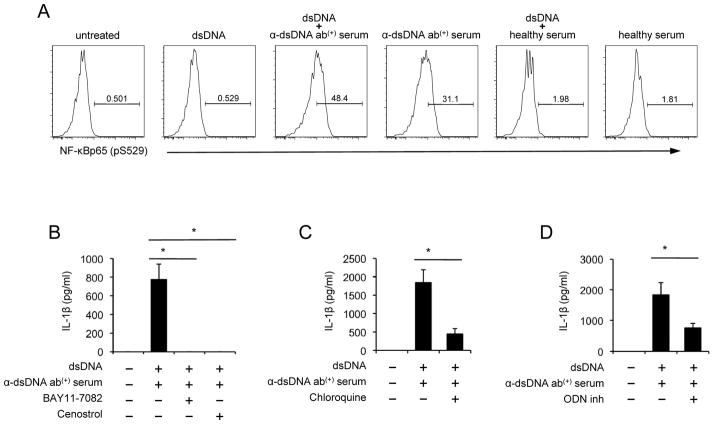
Figure 4. The production of IL-1β from human monocytes by self dsDNA and anti-dsDNA antibody-positive serum is dependent on TLR9 and NF-κB activation.
(A–D) Monocytes were purified from healthy donors for the following experiments. (A) Monocytes were incubated for 4 hours with dsDNA in the presence or absence of healthy or anti-dsDNA antibody-positive serum. NF-κB activation (phosphorylation) was determined by flow cytometry. Numbers in histograms indicate the frequency (%) of cells stained for phosphorylated NF-κB (pS529). (B–D) Monocytes were incubated for 18 hours with dsDNA and anti-dsDNA antibody-positive serum in the presence or absence of the NF-κB inhibitors (B, 5 μM Bay11-7082 and 5 μM Cenostrol), chloroquine (C, 5 μg/ml) or inhibitory nucleic acid sequence for TLR9 (D, 5 μM ODN). IL-1β in cell culture supernatants were measured by ELISA. Representative data from 4 independent experiments (A). Bars and error bars indicate mean and SEM, respectively (n = 4, 7 and 8 for B, C and D, respectively). *P < 0.05.