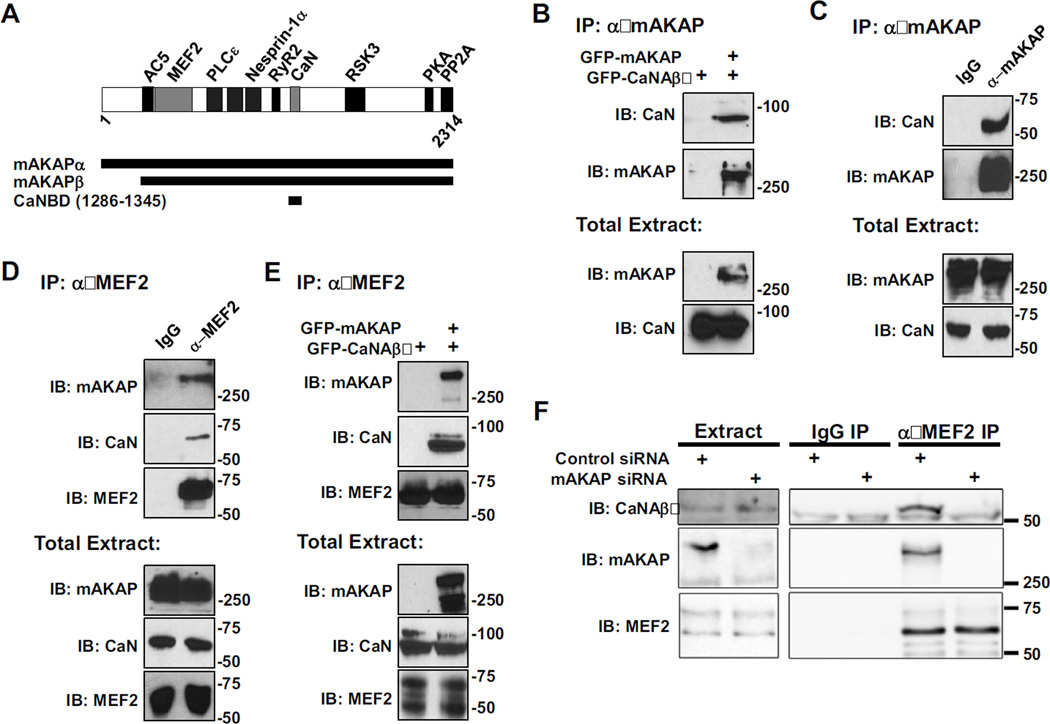
Figure 2. mAKAP is the scaffold for a signaling complex consisting of CaN and MEF2.
A) mAKAP domain structure. The stippled domains are the spectrin-like repeat domains [18–28]. Direct binding partners whose sites have been finely mapped in mAKAPβ are shown. mAKAPβ (the 227 kDa, alternatively-spliced isoform predominant in striated muscle) starts at residue 245 of mAKAPα (the 254 kDa, alternatively-spliced isoform predominant in neurons) [34]. All fragments are numbered per mAKAPα. B) Protein complexes were immunoprecipitated using a mAKAP antibody from HEK293 cells expressing GFP-tagged mAKAPβ (255 kDa) and CaNAβ (87 kDa). Protein in the immunoprecipitates (top panel) and in total extracts (bottom panels) were detected using CaN catalytic subunit and mAKAP-specific antibodies. C and D) Protein complexes were immunoprecipitated from C2C12 cell lysate using a mAKAP (C), MEF2 (D), or control IgG antibody and associated proteins were detected as in A. Note that like other AKAPs, mAKAP tends to migrate slower in SDS-PAGE than predicted by its molecular weight. E) MEF2 antibody was used to immunoprecipitate protein complexes from HEK293 cells expressing GFP-CaNAβ and GFP-mAKAPβ. CaN and MEF2 were associated in HEK293 cells only when co-expressed with mAKAP. F) MEF2 antibody was used to immunoprecipitate endogenous protein complexes from neonatal rat cardiac myocytes transfected with control or mAKAP-specific siRNA oligonucleotides. Endogenous CaNAβ (59 kDa) and mAKAPβ were present in MEF2 immunoprecipitates only when mAKAPβ was expressed. All blots shown are representative of experiments repeated at least three times.