Figure 2. Bim-deficiency rescues survival of Id2-deficient CD8+ T cells during infection.
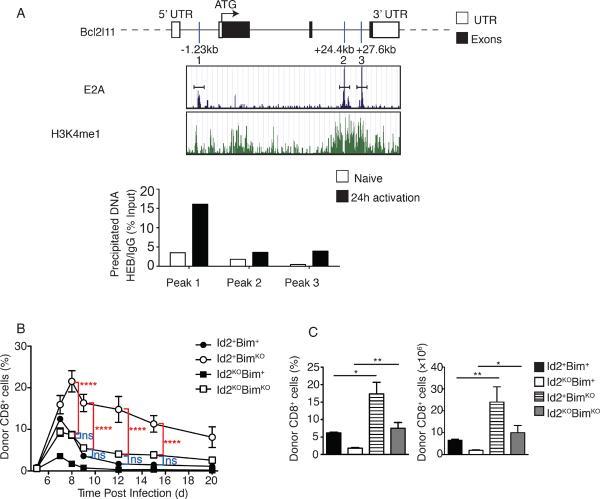
(A) E2A occupancy (blue peaks) and H3K4me1 occupancy (green peaks) for the Bcl2l11 gene as reported by Lin et al. (17). E box binding sites are indicated relative to the transcriptional start site (ATG = 0kb). Immunoprecipitation of chromatin (with anti-HEB or immunologlobulin G, IgG) isolated from purified OT-I Id2+ cells directly ex vivo or 24 h after in vitro activation with OVAp followed by quantitative PCR analysis of input or precipitated DNA for indicated E-box sites in the Bcl2l11 gene. Data are representative of two independent experiments, n = 3. (B) Percentage of CD8+ OT-I Id2+Bim+, BimKO, Id2KO or Id2KOBimKO CD45.2 over the course of infection in PBL. CD45.1+ C57BL/6 mice received OT-I Id2+Bim+, BimKO, Id2KO or Id2KOBimKO (CD45.2+) cells (2 × 104) 1 day before infection with Lm-OVA, average (±SEM). Two-way ANOVA analysis indicated no significant difference between expansion and contraction of Id2+Bim+ and Id2KOBimKO cells throughout the course of infection. These analyses also revealed significant difference between Id2+BimKO and Id2KOBimKO cells throughout the course of infection. . (C) Bar graphs summarizing frequency of donor cells among CD8+ cells and total number of indicated donor cells recovered from spleen on day 8 of infection. Statistical significance was determined using unpaired two-tailed t test where ns, not significant, *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.005, ***, P < 0.0005. Data are representative of three independent experiments with three mice per time point.
Knell et al.