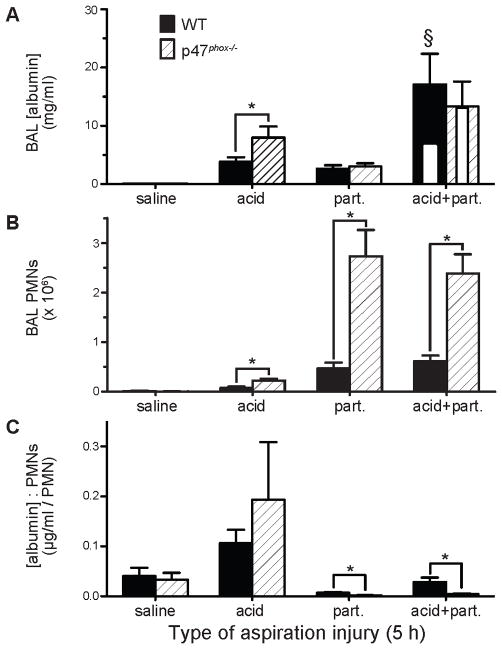
Figure 3. Effect of p47phox genotype on acid and gastric particulate aspiration-induced synergistic lung injury and inflammation.
Saline, acid, part., or acid+part. was instilled into the lungs, i.t., of WT and p47phox−/− mice. BAL was performed 5 h later and the recovered BAL was assessed for: A) albumin concentration ([albumin]), as an indicator of lung injury (white inset bars within the acid+part. data represent predicted values if injury was additive); B) PMN alveolitis; and C) ratio of BAL [albumin] to # of recovered PMN, an indicator of the degree of lung injury/PMN. N = 6 – 9 for each group from 7 independent experiments. * P < 0.05 for comparisons indicated by the brackets, § P < 0.05 for synergistic interaction of acid and particulate components within the indicated genotype by 2-way ANOVA (i.e., WT or p47phox−/− mice).