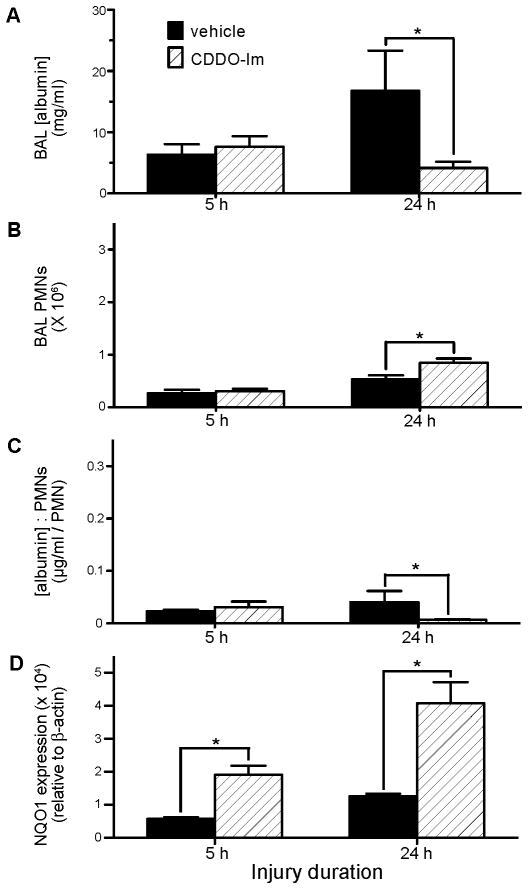
Figure 7. Effect of CDDO-Im treatment on acid and gastric particulate aspiration-induced lung injury, inflammation, and Nrf2-activated NQO1 expression.
WT mice were injured by i.t. instillation of acid+part. then treated 15 min later by i.p. injection of 100 μl of 2 mg/ml CDDO-Im in treatment vehicle (PBS + 10% DMSO + 10% cremaphor-EL) or vehicle alone. Mice were sacrificed and BAL performed at 5 and 24 h post-injury and recovered BAL analyzed for: A) [albumin]; B) PMN alveolitis; and C) ratio of BAL [albumin] to # of recovered PMN, an indicator of the degree of lung injury/PMN. D) In addition, the lungs were removed, homogenized, and separated into cytosolic and nuclear fractions. The cytosolic fraction was analyzed by Western blot, probed for NQO1 (a gene product under the control of the transcription factor Nrf2), and quantitated by fluorescence normalized to β-actin expression in each sample. N = 4 – 6 for each group from 1 experiment. * P < 0.05 for comparisons indicated by the brackets.