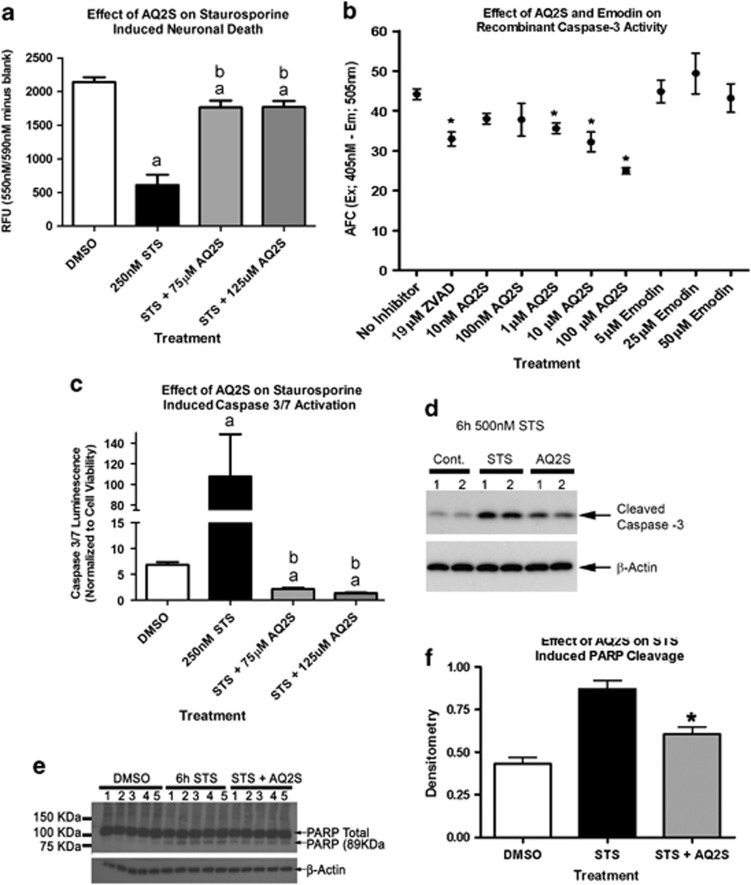
Figure 4.
AQ2S is a direct caspase-3 inhibitor. Primary rat cortical neurons were seeded onto a 96-well plate. (a) The effect of 24 h 250 nℳ STS on neuronal viability in the absence or presence of AQ2S (n=7/STS control injury, n=8/all other treatments). (b) The effect of AQ2S, Emodin, and ZVAD-fmk to inhibit recombinant activated caspase-3 as determined by inhibition of free AFC in a 96-well in vitro assay (n=7/no inhibitor, n=8/ZVAD-fmk, n=4 all other treatment groups). (c) The effect of 24 h 250 nℳ STS on neuronal caspase 3/7 activity the absence or presence of AQ2S (n=7/STS control injury, n=8/all other treatments). (d) Biochemical validation of caspase-3 inhibition in neurons after 6 h 500 nℳ STS+125 μM AQ2S (n=2/treatment). (e) PARP cleavage in neurons after 6 h 250 nℳ STS+125 μM AQ2S (n=5/treatment). (f) Densitometry of 89-KDa PARP cleavage fragment in STS+AQ2S-treated cells (n=5/treatment). Neuronal viability data, caspase-3 drug screening assay data, and PARP cleavage data were analyzed using one-way-ANOVA (P<0.0001; graphs show mean+S.E.M.). Neuronal caspase-3 data was transformed to log(Y) values and analyzed using one-way-ANOVA (P<0.0001 graphs show mean+S.E.M.). Letters and asterisks indicate significant (P<0.05) results of Fisher LSD post-hoc test. a=compared with no injury DMSO control (white bar). b=compared with injury only DMSO (black bar). Data was analyzed using one-way-ANOVA (P<0.0001; graphs show mean+S.E.M.)