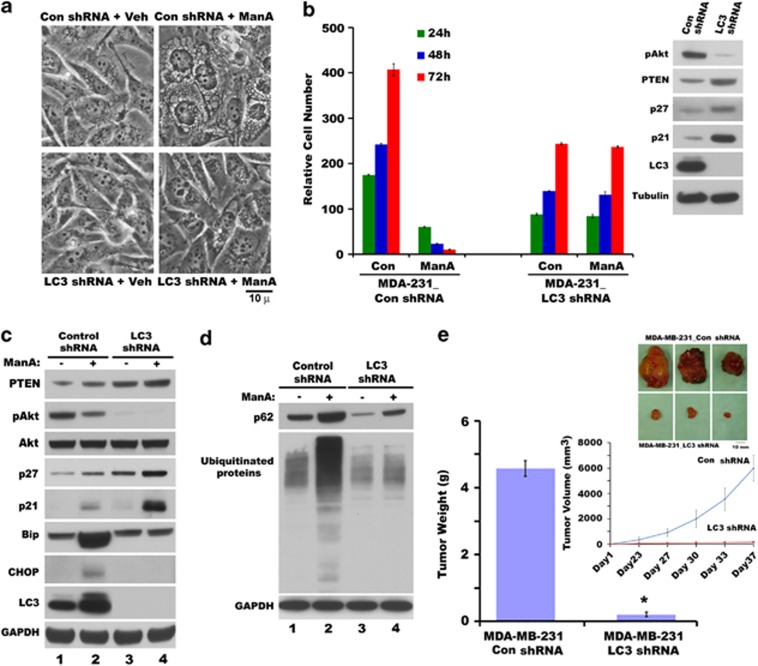
Figure 6.
LC3 deficiency reduces growth and protects from Man A-induced cytotoxicity of breast cancer cells. (a) Phase-contrast images of wild-type and LC3-deficient MDA-MB-231 cells treated with 5 μM Man A for 9 h. (b) LC3 deficiency in MDA-MB-231 cells decreased growth rate and protected from Man A-induced cytotoxicity. Inset represents pAkt, PTEN, p27, p21 and LC3 protein levels in MDA-MB-231 cells harboring control shRNA (Con shRNA) or LC3 shRNA expression vectors. (c) Western blot analysis of PTEN, pAkt, Akt, p27, p21, Bip, CHOP, LC3 and GAPDH in LC3-deficient MDA-MB-231 (LC3 shRNA) cells compared with control shRNA treated without or with Man A for 24 h. (d) Western blot analysis of p62, protein ubiquitination and GAPDH in LC3-deficient MDA-MB-231 (LC3 shRNA) cells compared with control shRNA cells treated without or with Man A for 24 h. (e) Reduced breast tumorigenic potential in vivo of LC3-knockdown cells (MDA-MB-231 LC3 shRNA) compared with control shRNA cells (MDA-MB-231 Con shRNA) as measured by tumor weight (*P<0.001). Inset shows relative sizes of tumors (top panel) and relative progression of tumor volumes (bottom panel) in xenografts derived from control shRNA (MDA-MB-231 Con shRNA) and LC3 shRNA (MDA-MB-231 LC3 shRNA)-expressing cells