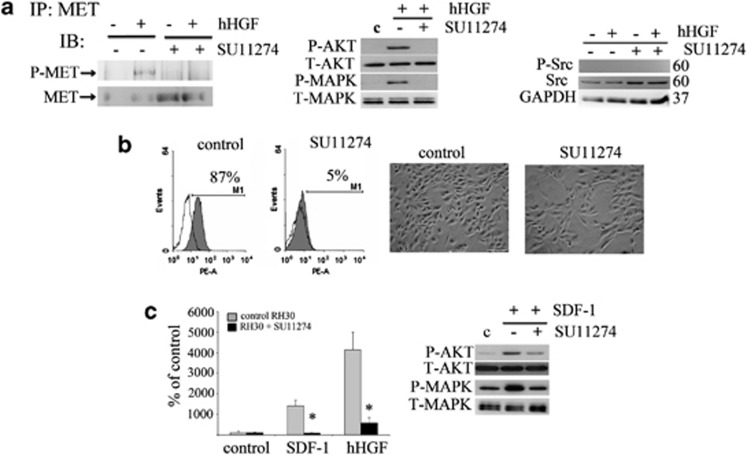
Figure 5.
Negative influence of the MET inhibitor (SU11274) on CXCR4 signaling. (a) The expression of phospho-MET after human HGF stimulation of control cells. Preincubation with SU 11274 abolished this phosphorylation. Phospho-MET was immunoprecipitated from 1 mg of protein extracts with an anti-MET antibody. Corresponding blots were developed after staining with anti-phospho-MET (Tyr 1234/1235) (left panel). Western blot analysis of AKT and MAPK activation in inhibitor treated cells showed a reduced activation of these signaling pathways following stimulation with 20 ng/ml human HGF (middle panel). Western blot analysis of phospho-Src showed no expression of this protein, whereas the total level of Src increased slightly after MET receptor inhibition using SU11274 (right panel). (b) Flow cytometry analysis of CXCR4 receptor expression and morphology assessment after inhibitor treatment. RH30 cells were treated with 5 μM of SU11274 for 16 h before experiments. The decrease in the level of surface expression was observed and the changes in the morphology of SU11274-treated cells were noted. Cells became more elongated and resembled differentiating cells. (c) The chemotactic analysis of RH30 cells. The ability of RH30 cells to migrate toward the human HGF (20 ng/ml) and SDF-1 (100 ng/ml) gradients was severely reduced after SU11274 treatment (left panel). Western blot analysis of AKT and MAPK phosphorylation after SDF-1 stimulation (100 ng/ml) showed a reduced activation of these signaling pathways following incubation with SU11274 (right panel). Western blot and FACS analysis was performed a minimum of three times and representative results are shown. The chemotaxis assay was performed three times in duplicates. Bar=50 μm; *P<0.05