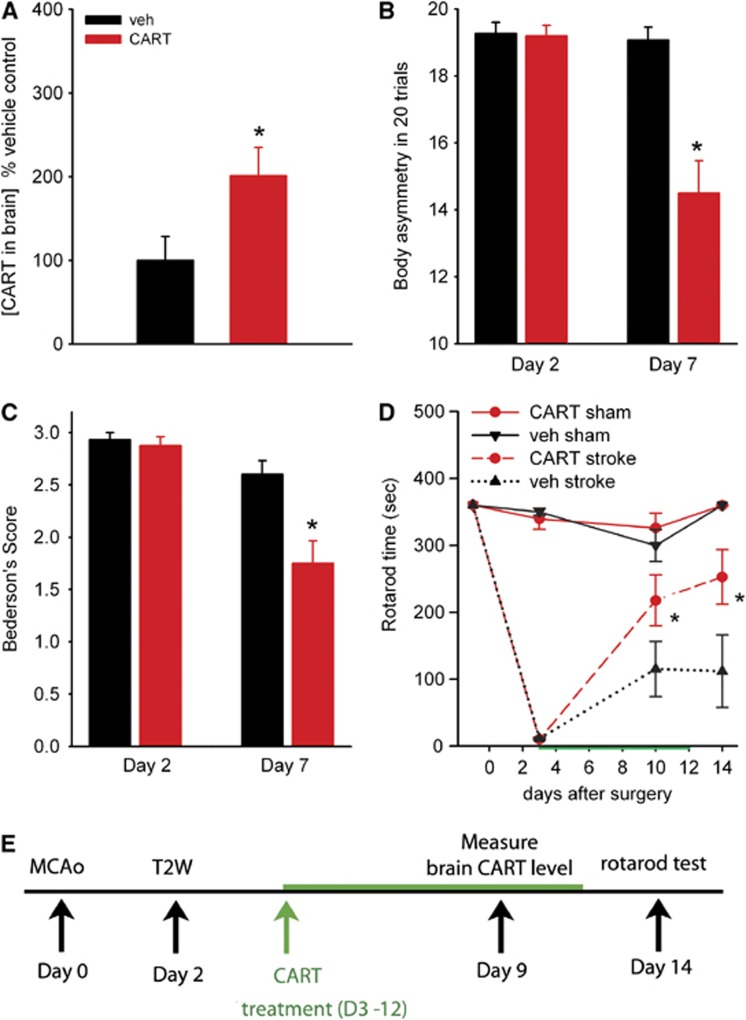
Figure 1.
Poststroke treatment with cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) improves behavioral recovery. (A) Intranasal delivery of CART increased brain CART concentration. CART (n=6) or vehicle (n=8) was delivered into nostrils of each rat at dose of 40 μL on day 3 after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo) and then 20 μL daily for another 6 days. Cerebral cortical tissue was harvested at 2 hours after the last dose of CART or vehicle. CART levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). All data were normalized to the mean CART level in the animals receiving vehicle. There is a significant elevation of brain CART protein level in animals receiving CART, compared with vehicle (P=0.04). (B) Poststroke treatment with CART improves behavioral recovery. Before intranasal treatment, all animals demonstrated close to 100% body asymmetry in 20 trials at 2 days after MCAo. CART treatment significantly reduced body asymmetry on day 7 post-MCAo (P<0.001). (C) Bederson's neurological tests were carried out on day 2 (before treatment) and on day 7 (after treatment). Intranasal CART treatment significantly reduced Bederson's score on day 7 post-MCAo (P<0.001). (D) Rotorod tests were taken before and days 2, 10, and 14 after MCAo or sham surgery. Treatment with CART significantly increased rotarod Etime in stroke animals (P=0.010, two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), *P=0.031, post-hoc Bonferroni test). Error bars show mean values±s.e.m. (E) Timeline of treatment.