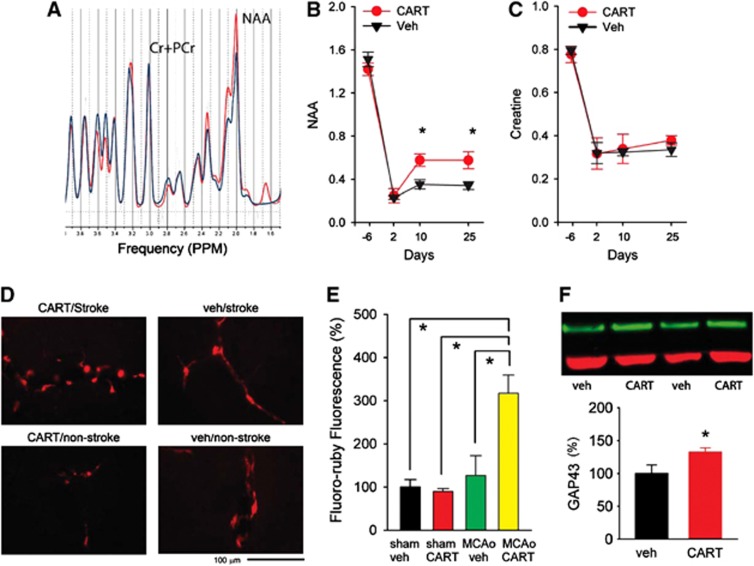
Figure 6.
Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART)-mediated changes in the lesioned side cortex. (A) Representative neurochemical tracings in the lesioned cortex from animals treated with CART (red tracing) or vehicle (blue tracing) measured by 1H-MRS (proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy) on day 25 after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo). (B, C) In 12 stroke animals studied, treatment with CART significantly increased acetylaspartate (NAA), but not the house-keeping signal creatine+phosphocreatine (Cr+PCr), in the lesioned side cortex on day 10 and 25 after stroke (*P<0.05, two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)). (D) Representative photomicrographs demonstrate an increase of fluoro-ruby fluorescence in the perilesioned cortex in a stroke rat receiving CART treatment. Fluoro-ruby tracer was administered to the lesioned side cortex on day 14 after MCAo or sham surgery. Fluorescence was examined on day 28 after stroke. (E) In 18 animals studied, intensity of fluorescence was analyzed by ImageJ and was normalized to the mean of control animals receiving vehicle treatment. A significant increase in fluoro-ruby fluorescence was found in stroke animals treated with CART, compared with all other groups (P<0.001, one-way ANOVA). No difference in fluorescence was found in nonstroke animals treated with CART or vehicle. (F) CART treatment significantly enhanced GAP43 immunoreactivity in the lesioned side cortex in 12 stroke rats (P<0.05, t test). GAP43 immunoreactivity was normalized to stroke animals receiving vehicle. Example of GAP43 Western blotting from four stroke rats (upper panel). Green: GAP43; Red: ACT.