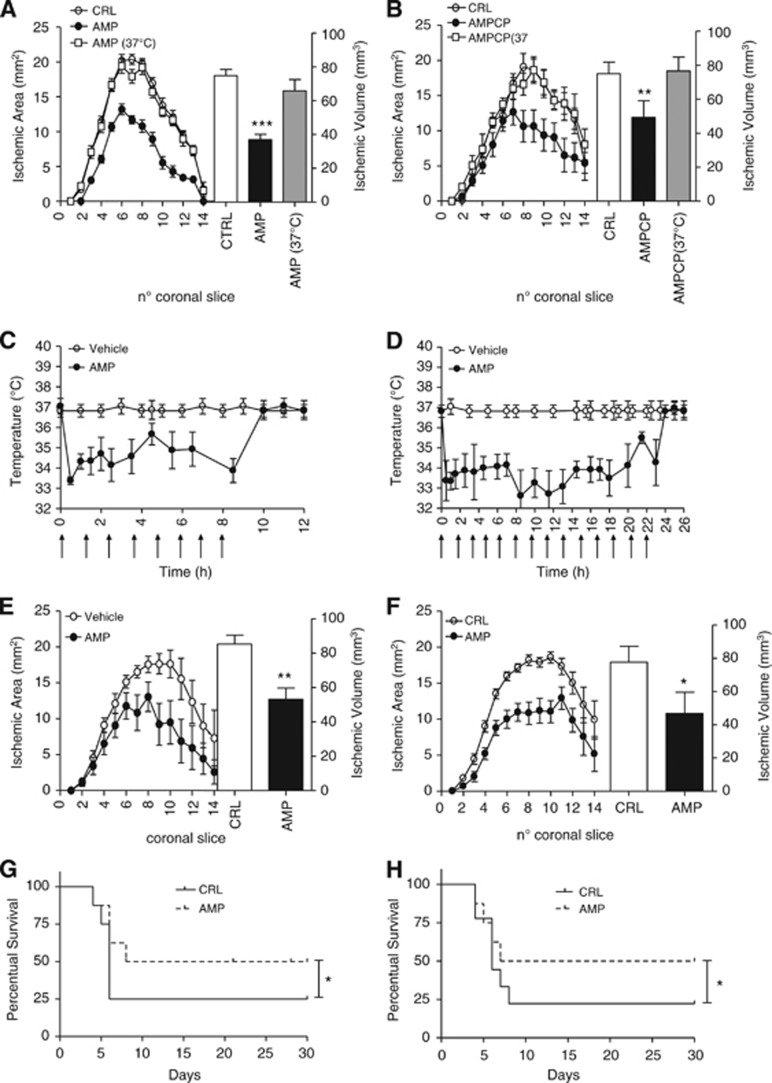
Figure 2.
Effect of 5′-adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and AMPCP on ischemic brain injury and survival in mice. Effect of intraischemic injection of AMP (50 mg/kg intraperitoneally) on brain infarct areas and volumes (A) of mice subjected to 1 hour middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo)/23 hours reperfusion. Ischemic neuroprotection is lost in mice receiving AMP and artificially kept at 37°C. Effect of intraischemic injection of AMPCP (50 μg intracerebroventricularly) on brain infarct areas and volumes (B) of mice subjected to 1 hour MCAo/23 hours reperfusion. Ischemic neuroprotection is lost in mice receiving AMPCP and artificially kept at 37°C. Body temperature (Tb) of mice subjected to 1 hour MCAo and posttreatment protocols of 10 hours hypothermia/24 hours reperfusion (C) or 24 hours hypothermia/72 hours reperfusion (D) obtained with AMP injections (arrows) of 50 mg/kg intraperitoneally every 90 minutes. The effect of posttreatment protocols of 10 hours hypothermia/24 hours reperfusion or 24 hours hypothermia/72 hours reperfusion on ischemic areas and volumes is shown in (E) and (F), respectively. Effects of protocols of intraischemic (G) or postischemic (24 hours) (H) hypothermia by AMP on survival of mice subjected to 1 hour MCAo. (A, B) Each point/column represents the mean±s.e.m., of at least eight animals per group. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 versus control (CRL). (E, F) Each point/column represents the mean±s.e.m., of at least eight animals per group. (G, H) Each line represents survival of groups of 10 ischemic mice. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 versus control (CRL).