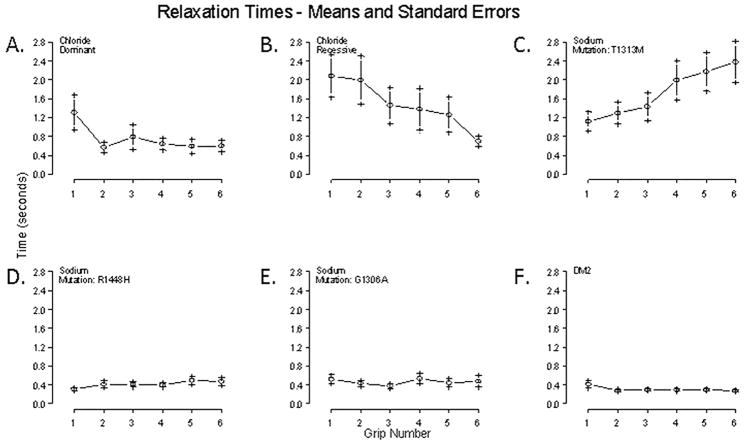
Figure 2.
90% to 5% relaxation times over sequential handgrips 1–6 for different mutation types. A. Subjects with dominant chloride channel mutations (n=11) show an increased 1st handgrip relaxation times with a pattern of warm-up of myotonia in subsequent handgrips. B. Recessive chloride channel subjects (n=10) show increased relaxations times compared to dominant, there is a pattern of warm-up in successive handgrips. C. Sodium subjects with the T1313M mutation (n=11) show paradoxical myotonia in successive handgrips. D. Subjects with R1448H mutations (n=5), on the other hand have essentially normal QMA relaxation times. E. No clear myotonia was demonstrated in subjects with G1306A mutations (n=5). F. Although there were no clear abnormalities on QMA for DM2 (n=6), in the group there is a subtle trend towards warm-up.