Figure 6.
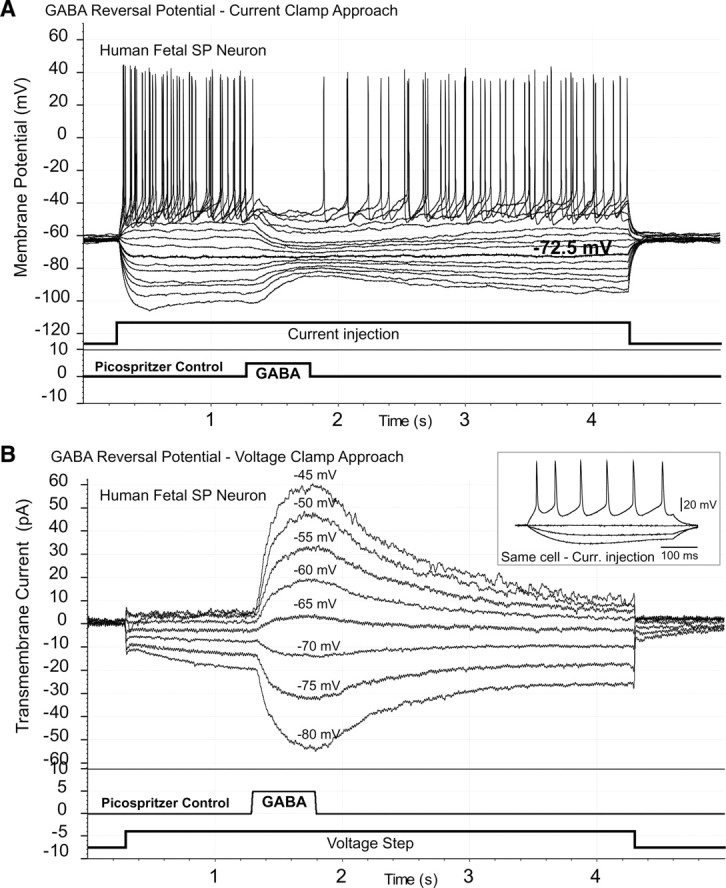
Reversal of the GABA-induced potential in human SP neurons. A, A set of 16 current pulses (current injection) was used to vary the membrane potential. Each time, a puff of GABA was delivered on the cell body using a computer-driven picospritzer. The GABA-induced postsynaptic potential reversed its polarity when the SP neuron was held at −72.5 mV (bold trace). B, An SP neuron was voltage clamped at different voltages starting from −80 mV, in 5 mV increments (voltage step). At each voltage step, one GABA puff was locally applied. The reversal of GABA current polarity occurred between −70 mV and −65 mV. Inset, This same cell fires repetitive APs upon direct current stimulation.
