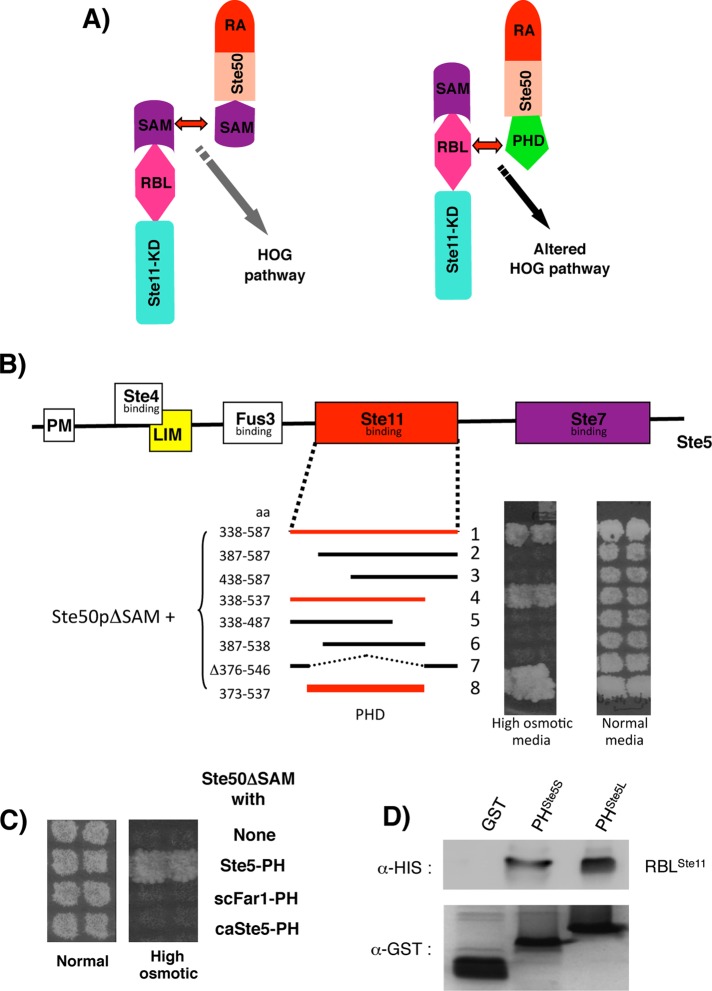
FIGURE 3:
Ste11 interacts with the PHSte5 domain. (A) Schematic representation of the interaction of Ste11 with Ste50 through their respective SAM domains in the natural HOG pathway (left) and through the RBL and grafted PHSte5 domain in the altered HOG pathway. (B) The altered HOG pathway format in A was used to delineate the boundary of the PHSte5 domain in yeast strain YCW1476 (ste50Δ ssk2Δ ssk22Δ) by monitoring its ability to grow on hyperosmotic media (with 0.75 M NaCl). (C) The RBLSte11 domain specifically interacts with the PHSte5 domain. Other PH domains replacing the Ste50-SAM domain were unable to activate the altered HOG pathway, indicating that they do not interact with the RBLSte11 domain. (D) The RBLSte11 domain interacts with the PHSte5 domain in vitro. Bacterially expressed, His-tagged RBLSte11 was incubated with glutathione–Sepharose bead–immobilized Ste5 fragments of either aa 373–537 (PHSte5L) or 373–523 (PHSte5S) as GST fusion or GST alone as control. His-tagged BRLSte11 copurified with the glutathione–Sepharose beads was revealed by Western blotting analysis with anti-His antibody (top) and the GST fusion with anti-GST antibody (bottom).