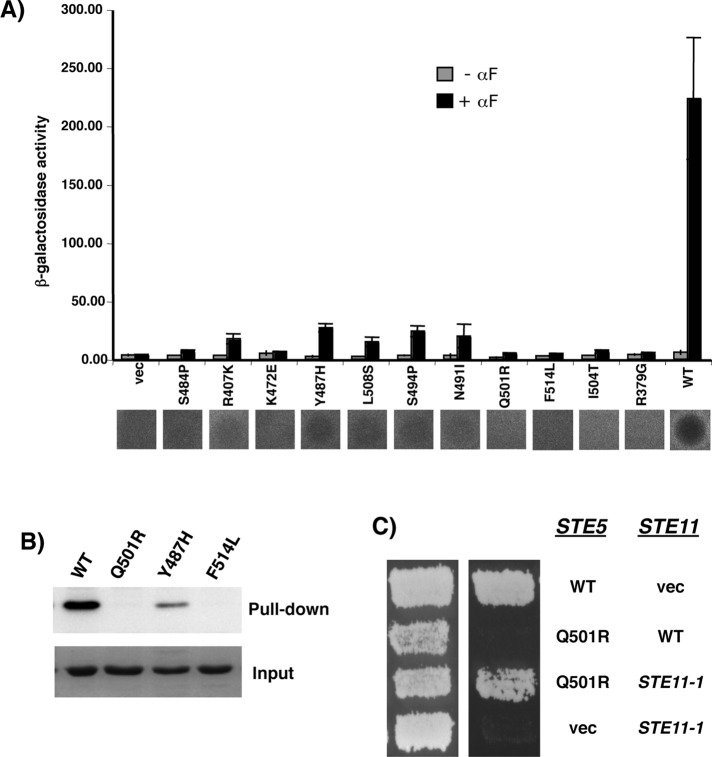
FIGURE 4:
Mutational analysis of the essential role of the PHSte5 domain in pheromone response. (A) β-Galactosidase assay (top) and Halo assay (bottom) of yeast cells (ste5Δ) transformed with STE5 alleles carrying mutations in the PH domain for their ability to induce pheromone-dependent transcriptional activation of mating-specific reporter gene and cell cycle arrest. (B) Pull-down assay with bacterially expressed GST-RBLSte11- and His-tagged PHSte5-domain mutants. Western blot analysis of pull-down and input of PHSte5-domain mutants was carried out with anti-His antibody. (C) Activated STE11 allele bypasses the mating defect of the PHSte5-domain mutant. Yeast cells (ste5Δ) cotransformed with either STE5 or STE11 allele or vectors in combination as indicated were assayed for their ability to mate, and the mating products were revealed on selective medium (right).