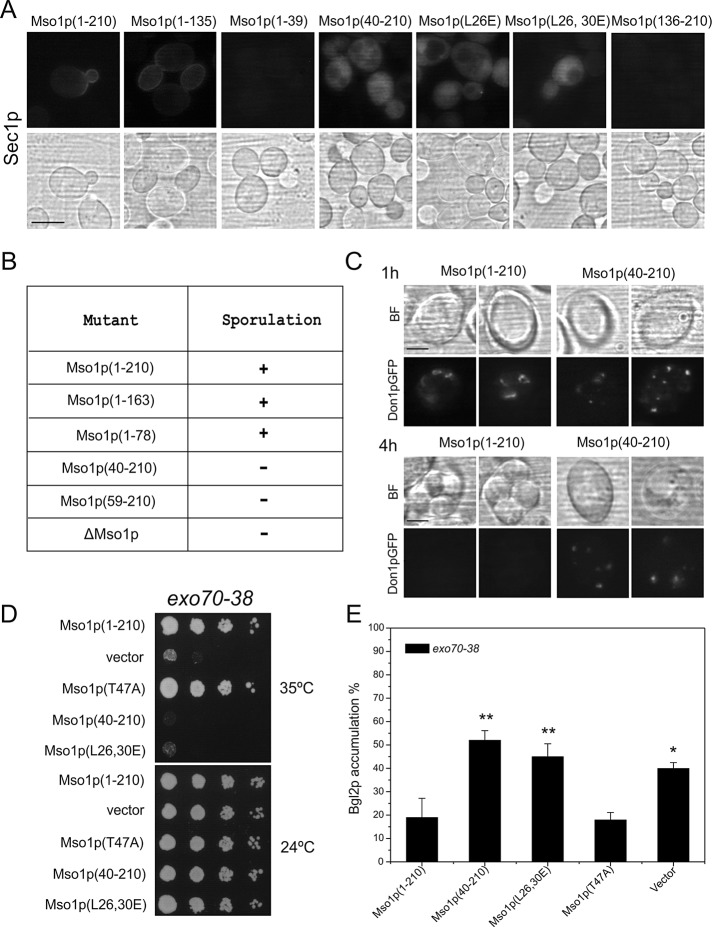
FIGURE 3:
The N-terminus is important for Mso1p in vivo function. (A) Localization of the Mso1p–Sec1p BiFC signal in vivo. Haploid, vegetatively grown wild-type cells (H304) coexpressing the indicated YFP(C)-tagged Mso1p variants with Sec1p-Venus(N) investigated by fluorescence microscopy. Scale bar, 5 μm. (B) The sporulation ability of cells expressing different Mso1p mutants. (C) Localization of Don1p-GFP and spore formation in MSO1 wild-type and mso1(40-210) diploid cells. Scale bar, 2 μm. (D) Mso1p N-terminus is required for multicopy suppression of the temperature-sensitive growth of exo70-38 cells. exo70-38 (H3742) cells were transformed with plasmids expressing different versions of Mso1p, followed by monitoring of cell growth at indicated temperatures. (E) Mso1p membrane insertion is functionally important for protein secretion in exo70-38 cells. Bgl2p accumulation was measured by Western blotting from lysates prepared from exo70-38 cells grown at 37°C expressing different versions of Mso1p. Error bars represent SD (minimum of three independent experiments). Student’s t test, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.