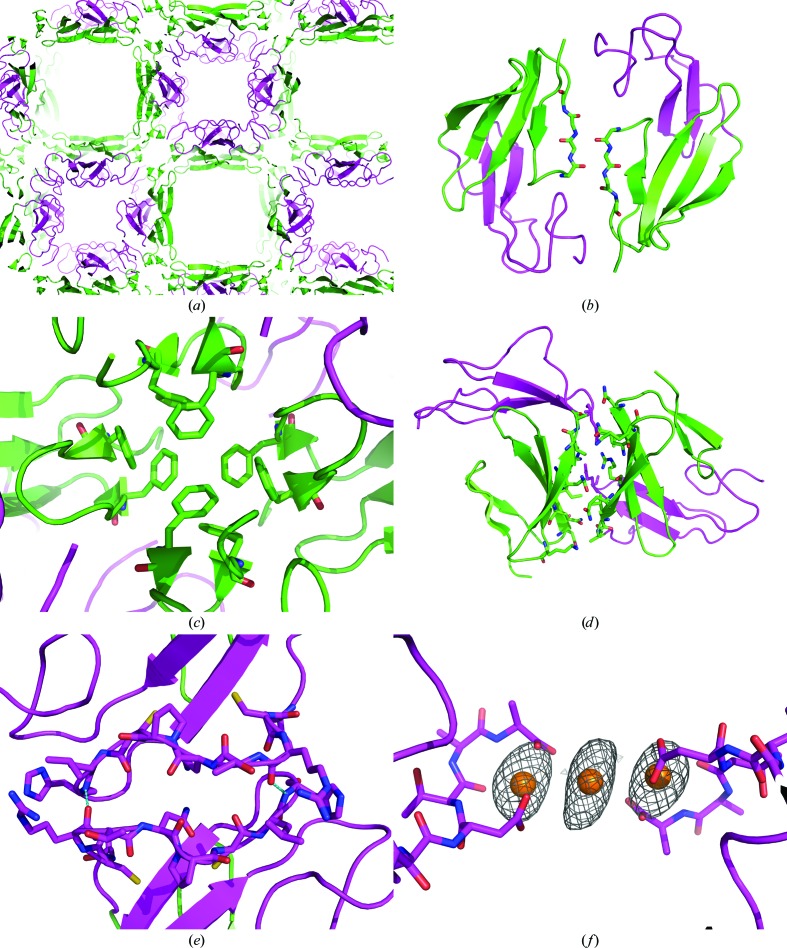
Figure 4.
The packing of FXII-FnIE viewed along the c axis shows large solvent channels (a): one lined by the EGF domain (magenta) and the other lined by β-strand E of the FnI domain (green). The FnI domain makes extensive crystal contacts on two sides of the domain (b, c, d), whereas the EGF domain has only one crystal-packing interface on a twofold axis, stabilized by a hydrogen bond between Arg160 O and His166 N and depicted in cyan (e). Some of the contacts made by the FnI domain are remarkable; the N-terminal β-sheet extends itself with a symmetry-related β-sheet (b) and a tetramer is formed via stacking of phenylalanine side chains (c). In the holmium-bound structure two symmetry-related FXII-FnIE molecules are connected via a holmium cluster of three Ho atoms (f). The Ho atoms are shown with the coordinating protein atoms and the anomalous map is contoured at an r.m.s.d. of 4; other coordinating atoms, such as water, are not displayed because their positions are uncertain.