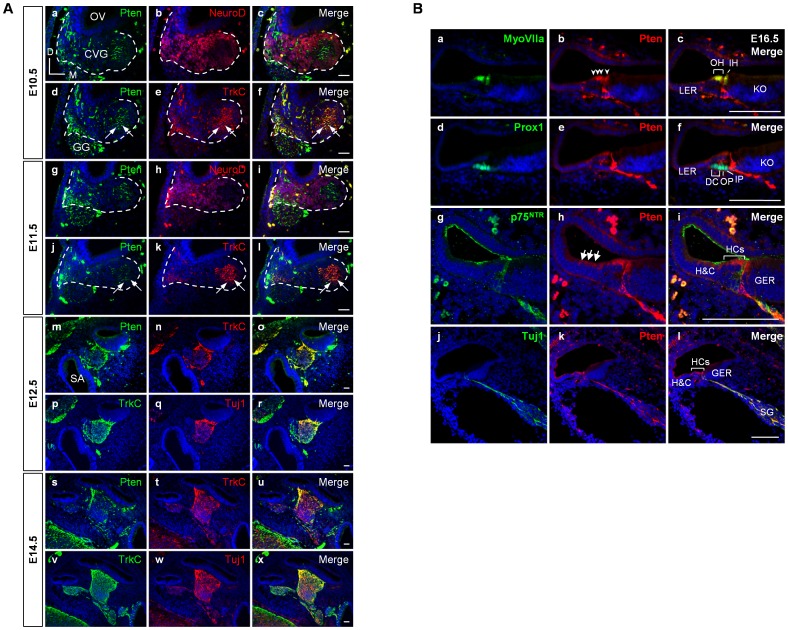
Figure 1. Pten expression patterns during inner ear development.
(A, B) Pten expression in the inner ear was examined by immunofluorescence at E10.5, E11.5, E12.5, E14.5, and E16.5. (A) Pten protein (green) was first detected between E10.5 and E11.5 in the cytoplasm of the cochleovestibular ganglion (CVG) complex (white outlines in a–l), and mainly overlapped with TrkC-positive neural precursor cells (red) rather than co-localizing with NeuroD (red) (arrows in a–l). From E12.5 to E14.5, Pten (green) was clearly expressed in TrkC-positive cells (red) in cochlear ganglion neurons, which were defined by Tuj1-positive ganglia (red) (m–x). DAPI-stained nuclei (blue) are seen in all images. CVG, cochleovestibular ganglion; D, dorsal; GG, geniculate ganglion; M, medial; OV, otic vesicle; SA, saccule. Scale bars: 100 µm. (B) At E16.5, Pten-immunopositive signals (arrowheads in b) were observed in the MyoVIIa-positive hair cells (green) (a–c) but not in the Prox1-positive supporting cells (green) (d–f). Expression of Pten was detected in the Hensen’s and Claudius’ cells (arrows in h), Tuj1-positive neurons (green), but not in p75NTR-positive pillar cells (green) (g-i). DAPI-stained nuclei (blue) are seen in all images. DC, Deiter’s cell; GER, greater epithelial ridge; H&C, Hensen’s and Claudius’ cells; HCs, hair cells; IH, inner hair cell; IP, inner pillar cell; KO, Kölliker’s organ; LER, lesser epithelial ridge; OH, outer hair cell; OP, outer pillar cell; SG, spiral ganglion. Scale bars: 100 µm.