Figure 2. Inner ear phenotypes in Pten conditional knockout (cKO) mice.
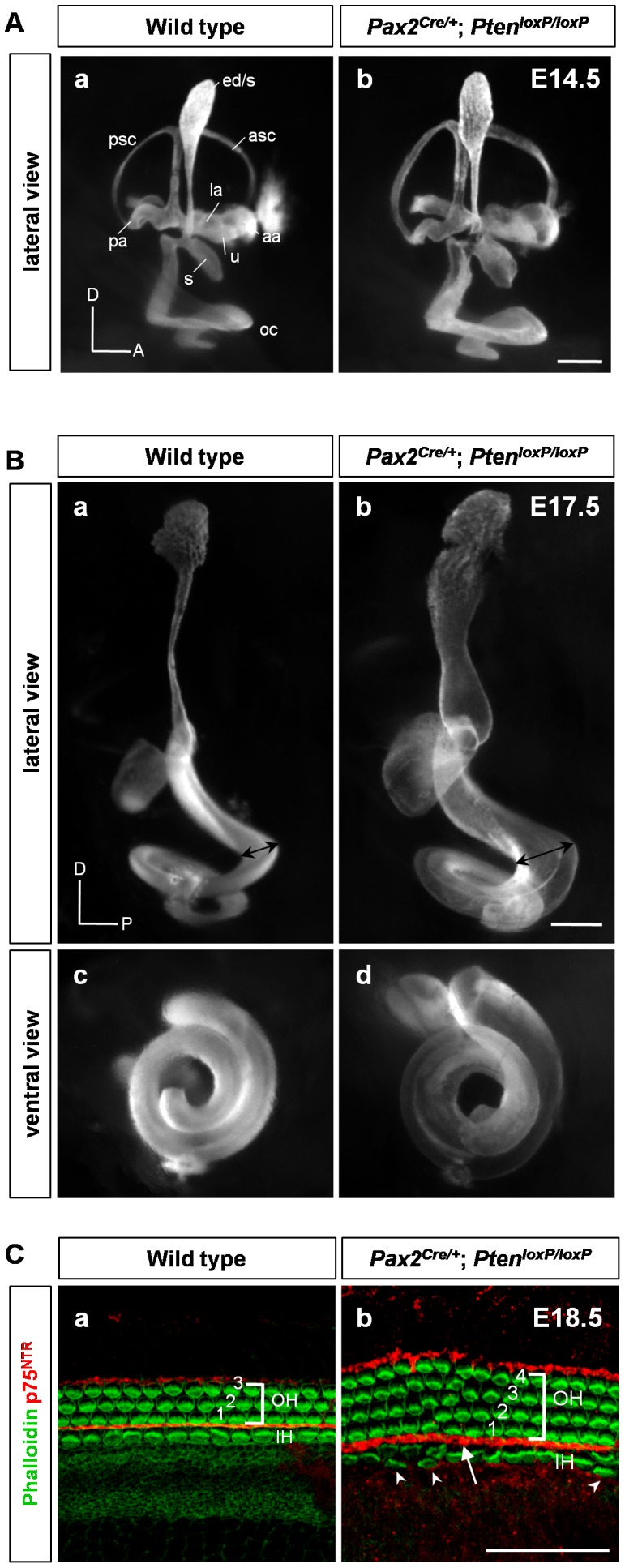
(A) Paint-filled inner ears of Pten cKO embryos at E14.5 shown in a lateral view. Pten-deficient inner ears showed abnormal morphology in the vestibule, including a thickened semicircular canal and canal pouches with a widened endolymphatic duct and common cruses. There was a grossly widened morphology with a coarse pattern in the cochlea. aa, anterior ampulla; asc, anterior semicircular canal; ed/s, endolymphatic duct and sac; la, lateral ampulla; oc, organ of Corti; pa, posterior ampulla; psc, posterior semicircular canal; s, saccule; u, utricle; A, anterior; D, dorsal. Scale bar: 50 µm. (B) At E17.5, the Pten deletion-induced morphology became more evident compared to that in the wild type (black double arrow in a, b). D, dorsal; P, posterior. Scale bar: 100 µm. (C) The morphological pattern of the epithelium was analyzed by whole-mount phalloidin with p75NTR immunofluorescence. Pten-deficient mice showed additional rows of outer and inner hair cells, whereas wild-type mice showed three rows of outer hair cells and one row of inner hair cells at E18.5 (arrowheads in b). p75NTR-positive pillar cells were irregular and widened compared to those in wild-type mice (arrow in b). IH, inner hair cell; OH, outer hair cell. Scale bar: 100 µm.
