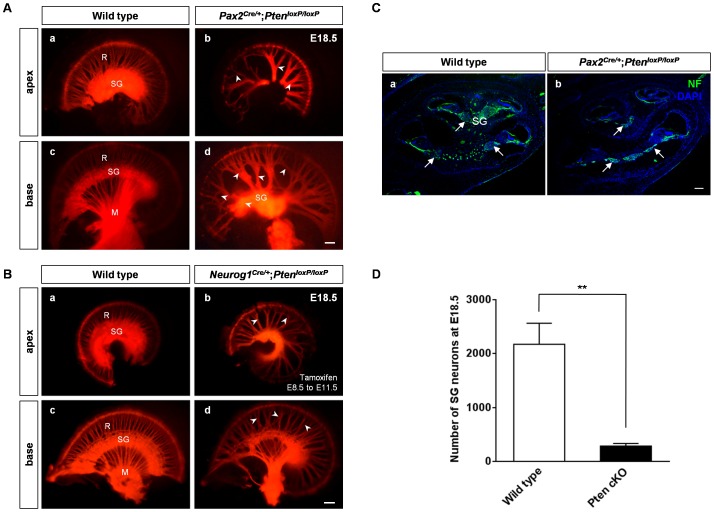
Figure 3. Cochlear innervation defects in Pten-deficient mice.
(A, B) Patterns of cochlear innervation were assessed by NeuroVue-tracing at E18.5. (A) In Pax2Cre/+;PtenloxP/loxP mice, nerve innervation was evident in the apical and basal turns of the cochlea in wild-type (a, c) and Pten cKO (b, d) mice. Pten-deficient inner ears displayed sparse radial fibers, a disorganized pattern, and loss of spiral ganglia in the cochlea (arrowheads in b, d). Abnormal innervation was distributed evenly throughout the cochlea. M, modiolus; R, radial fibers; SG, spiral ganglion. Scale bar: 100 µm. (B) Neurog1Cre/+;PtenloxP/loxP mice were administered tamoxifen as an IP injection to perform tamoxifen-inducible deletion of Pten between E8.5 and E11.5. Neuronal abnormalities were seen in Pax2Cre/+;PtenloxP/loxP mice and similar innervation defects in Neurog1Cre/+;PtenloxP/loxP mice revealed spacing or several gathered radial fibers and a disorganized pattern in the innervation of the cochlea (arrowheads in b, d). The innervation defects were distributed evenly throughout the cochlea. M, modiolus; R, radial fibers; SG, spiral ganglion. Scale bar: 100 µm. (C, D) Neuronal loss in the spiral ganglion in Pax2Cre/+;PtenloxP/loxP mice at E18.5. (C) Neurofilament immunoreactivity (arrows) and (D) the number of the spiral ganglia were significantly decreased in Pten cKO mice compared to wild-type mice at E18.5 (3 cochleae, P<0.01). M, modiolus; R, radial fibers; SG, spiral ganglion. Scale bar: 100 µm.